When we talk about water quality, we often focus on what we can see, like clarity, or what we can taste, like salt. But the most critical factor for life and industrial efficiency is something invisible: Dissolved Oxygen (DO).
Many operators and engineers start their journey by asking, “What is dissolved oxygen in water?” and why does it fluctuate so drastically? At Sino-Inst, we’ve seen how answering this question through precise DO monitoring can save a fish farm from total loss or reduce a wastewater plant’s energy bill by over 30%. In this guide, we will decode the science behind oxygen solubility and show you how to master this vital water sign.

What Is Dissolved Oxygen in Water? (The “Breath” of Water)
What is oxygen that is dissolved in water?
In simple terms, it is the amount of oxygen (O₂) that is dissolved in a liquid. Unlike the oxygen atoms that make up the molecule of water (H₂O), dissolved oxygen is made up of molecules that float in water and can be used by living things and chemicals.It’s like the “atmosphere” under the water. To live, we need oxygen in the air. Microbes in water and in factories also need these dissolved molecules to “breathe.”
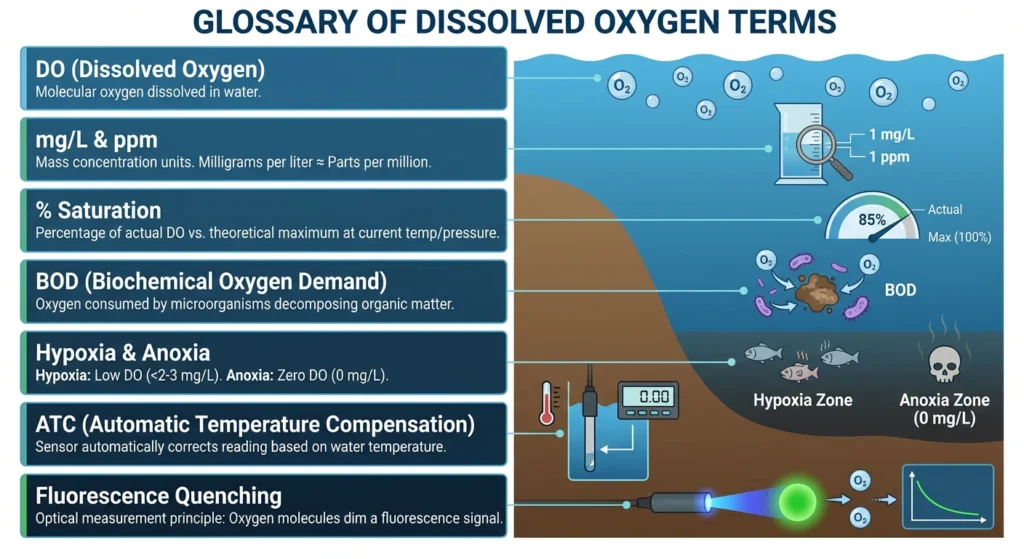
The Oxygen Balance: Sources vs. Sinks
To manage what is dissolved oxygen in water effectively, you must understand the “In and Out” of gas exchange.
🌊 How Oxygen Enters (Sources)Atmospheric Diffusion:
- Oxygen naturally crosses the surface. The rougher the water (waves/rapids), the more it “breathes.”
- Photosynthesis: Aquatic plants release pure O₂ during daylight hours.
- Mechanical Aeration: In industrial tanks or fish farms, blowers and diffusers force oxygen into the water to maintain life.
📉 How Oxygen Is Lost (Sinks)Respiration:
- Fish, plants (at night), and microbes constantly consume O₂.
- Decomposition (BOD): Bacteria use up massive amounts of oxygen while breaking down organic waste.
- Rising Temperature: As water heats up, it physically loses its ability to hold gas, forcing oxygen out.
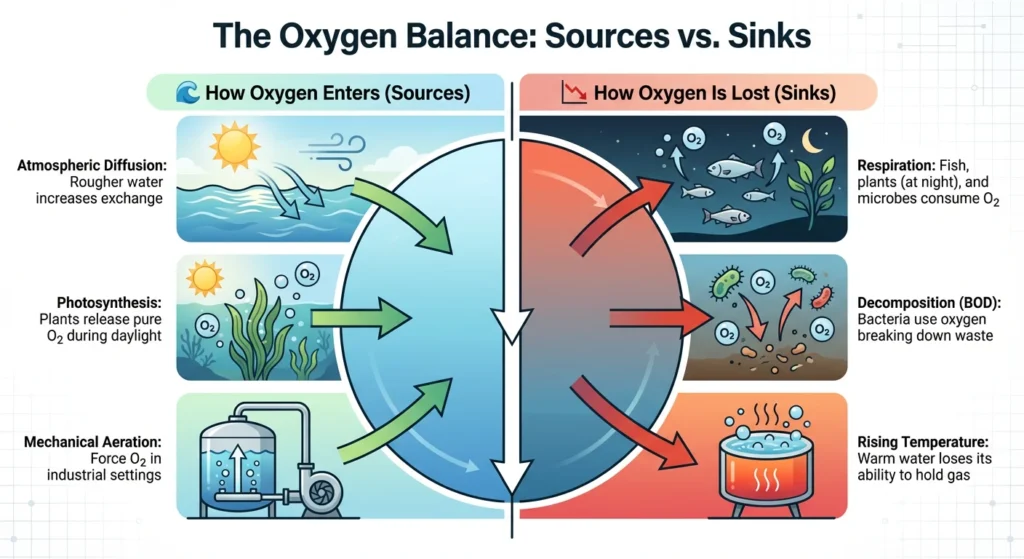
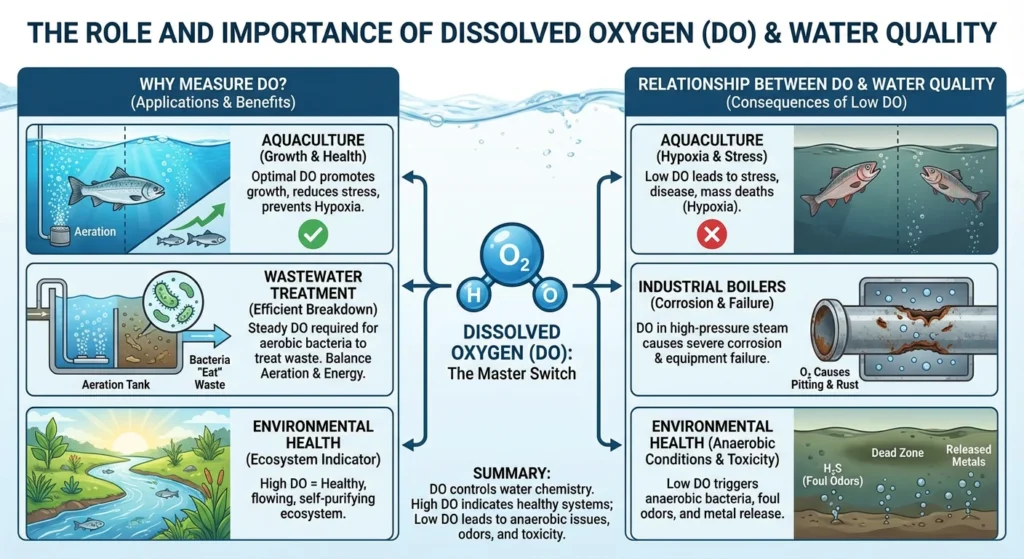
The Role and Importance of DO: Why Measure It?
DO monitoring isn’t just interesting from a science point of view; it’s also necessary for safety and financial reasons in many fields:
- Aquaculture: DO is the main thing that makes fish grow. If levels drop too low, called hypoxia, stress, sickness, and mass deaths happen.
- Using aeration tanks to treat wastewater means that special bacteria can “eat” organic garbage. For these bacteria to work, they need a steady flow of DO. Too much aeration uses a lot of electricity, and too little aeration stops the treatment process.
- When it comes to industrial boilers, DO is bad because it makes high-pressure steam worse. Even very small amounts of oxygen can cause metal pipes to pit and rust, which can cause severe equipment failure.
- Environmental Health: DO is the best way to tell how healthy a body of water is. People often know when levels are low because of nutrient waste or “Dead Zones.”
The Relationship Between DO and Water
Quality Dissolved oxygen is the “Master Switch” for water chemistry.
- High DO usually indicates a healthy, flowing ecosystem capable of self-purification.
- Low DO triggers the growth of anaerobic bacteria, which produce foul odors (like rotten egg gas, H₂S) and release trapped heavy metals from the sediment back into the water.
Factors That Affect Dissolved Oxygen (The Solubility Logic)
Understanding what is dissolved oxygen in water requires knowing what controls its solubility. Water is like a sponge—it can only hold so much:
- Temperature (The #1 Factor): Cold water holds significantly more oxygen than warm water. This is why fish kills often happen during hot summer nights.
- Atmospheric Pressure: Higher pressure (at sea level) forces more oxygen into the water than at high altitudes.
- Salinity (The Salt Effect): Saltwater holds about 20% less oxygen than freshwater because the dissolved salts take up the “space” oxygen molecules would occupy.
- Biological Demand: Photosynthesis by plants adds oxygen during the day, while respiration and decay consume it at night.
Want to see how temperature acts as a ‘Sink’ for your water’s oxygen capacity? Try our simulator below!
🐟 Dissolved Oxygen “Survival” Sim
Adjust the temperature to see how much oxygen the water can actually hold.
*Calculated at sea level (1 atm). Real-time monitoring by Sino-Inst ensures your levels stay safe!*
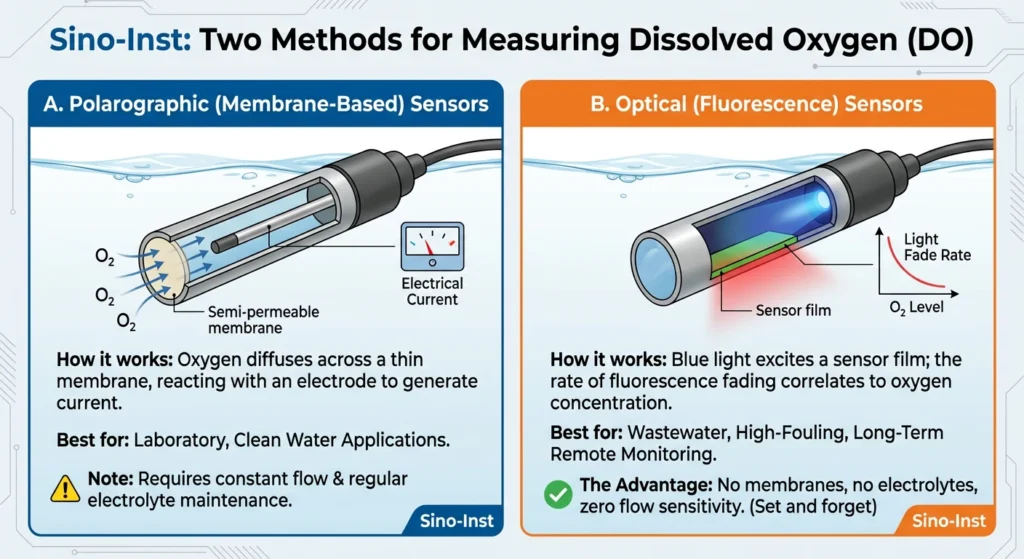
How to Measure Dissolved Oxygen: Choosing the Right Technology
As a leader in process monitoring, Sino-Inst offers two primary ways to measure DO. Choosing the right DO controller depends on your environment:
A. Sensors that use polarography (membrane-based)
- How it works: Oxygen moves across a thin membrane and reacts with an electrode to produce an electrical current.
- Best for: Laboratory settings or clean water applications.
- Note: These require a constant flow of water and regular electrolyte maintenance.
B. Optical (Fluorescence) Sensors
- How it works: A blue light makes a sensor film react, and the rate at which the light “fades” is directly related to the amount of oxygen in the air.
- Best for: Wastewater, high-fouling environments, and long-term remote monitoring.
- The Advantage: No membranes, no electrolytes, and zero flow sensitivity. This is the “set and forget” solution for modern industry.
Conclusion:
Data is better than gut feelings when it comes to managing water quality.
Going back to our main question: What is dissolved oxygen in water? It is more than simply a number; it is the “vital pulse” of your water ecosystem and the “safety switch” of your industrial infrastructure.
💡 Important Things to Keep in Mind:
Accuracy is important: Dissolved oxygen changes a lot with changes in temperature and pressure. Your firm can’t afford to take the chance of relying on “feeling” or old-fashioned tests.The Technology Shift: Optical (Fluorescence) technology, like our DSD-160W, is quickly taking over the market since it doesn’t drift and doesn’t need much maintenance.
Unit Logic: Use % Saturation to keep an eye on the health of your plants and mg/L (ppm) to make sure you’re using the least amount of energy possible when aerating.
FAQ
Related Products
Stop Guessing. Start Monitoring with Sino-Inst.Whether you are managing a massive wastewater treatment plant, protecting a million-dollar aquaculture harvest, or preventing corrosion in high-pressure boilers, Sino-Inst has the specialized tools to ensure your water quality stays within the “Goldilocks Zone.”🚀
Don’t wait for a low-oxygen disaster or a high-cost energy bill to take action. Join thousands of engineers who trust Sino-Inst for precision water analysis.
Request A Quote
More Resources
-
The 10 Best Digital carbon monoxide detectors 2026: An Industrial Guide
Carbon monoxide (CO) remains one of the most hazardous invisible threats in industrial, commercial, and residential environments. Colorless, odorless, and tasteless, it requires…
-
Can gas detectors detect multiple gases simultaneously?
In the complex and often hazardous world of industrial manufacturing, petrochemical processing, and confined space operations, ensuring the safety of personnel is the…
-
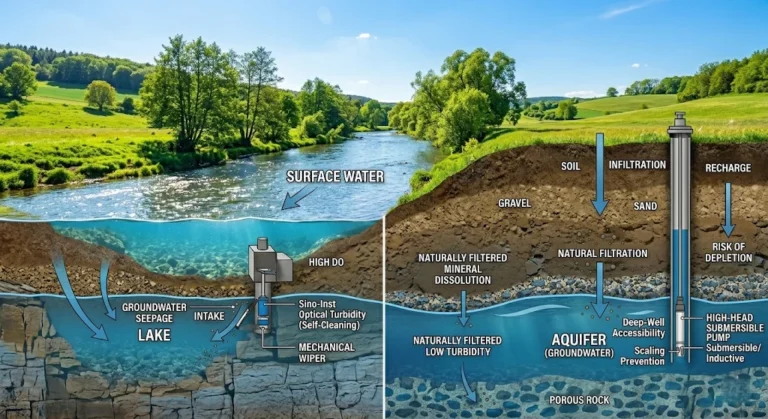
Surface Water vs Groundwater: A Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality
In the domains of environmental engineering and industrial water management, knowing the basic differences between surface water vs groundwater is not just an academic…
-
What is the pH of Reverse Osmosis Water? The Complete Science Guide (2026)
If you have ever been curious about ‘what is the pH of reverse osmosis water?’, you are not alone. This is one of…
-
The Top 8 Portable CO Detector for Car Use
Introduction: The Silent Threat in Automotive Cabins Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas generated by the incomplete combustion…
-
6 Best Mass Flow Controller for Liquids: An Expert Technology Guide
In modern industrial automation, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor fabrication, the precise control of fluid dynamics is a fundamental requirement. Relying on outdated volumetric…
.png)