Introduction:Why the Chlorine”Guess”Costs You Money?
In water treatment,precision isn’t just a goal;it’s a safety requirement.Many operators ask:”Is total chlorine vs free chlorine same?“The short answer is no.Mistaking one for the other can lead to failed disinfection,excessive chemical waste,or even regulatory fines.
At Sino-Inst,we’ve seen how understanding free chlorine vs total chlorine can transform an inefficient plant into a high-performance system.This guide breaks down the invisible chemistry to help you make informed decisions for your process.

The Chlorine Formula You Need to Know
In pool chemistry, chlorine exists in three distinct states. The relationship between them is defined by this simple equation:
Total Chlorine = Free Chlorine + Combined Chlorine
Free Chlorine (The “Active Hero”)
- Free Chlorine (FC) is the amount of chlorine that has not yet combined with contaminants. This is your active sanitizer. It is responsible for killing bacteria, viruses, and neutralizing organic matter.
- Ideal Range: 1.0 – 3.0 ppm.
- Goal: This is the most important number to track.
Combined Chlorine (The “Inactive Waste”)
Combined Chlorine (CC), also known as chloramines, forms when Free Chlorine reacts with contaminants like sweat, oils, or ammonia. CC has no sanitizing power; instead, it causes eye irritation and that distinct “pool smell.”
- Ideal Range: Less than 0.2 ppm.
- Warning: If CC exceeds 0.5 ppm, your pool needs a “Shock” treatment.
Total Chlorine (The “Total Sum”)
Total Chlorine (TC) is simply the sum of the two above. A high TC reading is misleading—if your TC is 3.0 but your FC is only 0.5, your water is actually unsafe and under-sanitized.

Comparison: Total Chlorine vs Free Chlorine
| Feature | Free Chlorine (FC) | Total Chlorine (TC) |
| What it is | The amount of active chlorine available to kill bacteria and algae. | The total sum of all chlorine currently in your water. |
| Formula | $FC = TC – Combined\ Chlorine$ | $TC = FC + Combined\ Chlorine$ |
| Role in Safety | The Protector: It is the only form that keeps water safe and clear. | The Indicator: A general number that doesn’t show sanitizing power. |
| The “Smell” Test | No strong odor. High FC is safe and clean. | If TC is high but FC is low, you get a heavy chemical smell. |
| Ideal Range | 1.0 – 3.0 ppm | Must be checked alongside FC to ensure balance. |
| Best Testing Tool | [Sino-Inst Digital FC Sensor] for 0.01 precision. | Standard DPD kits or TC sensors. |
5 Critical Differences: Why It Matters for Your Business
The key to good water management is knowing the differences between free chlorine and total chlorine.
Disinfection Power: Active Killer vs. Weak Residual
Free chlorine is the “workhorse.” It is 25 to 100 times more effective at killing pathogens than combined chlorine. If your total chlorine is high but your free chlorine is low, your water may still be biologically unsafe.
The “Chlorine Smell” Myth: How It Affects Your Senses
People often say, “The water smells like chlorine, so there must be too much of it.” Reality: That pungent smell is caused by combined chlorine (chloramines). A strong smell actually indicates you have too little free chlorine to break down the waste.
Reaction Speed: Instant Impact vs. Slow Release
Free chlorine provides an instant kill. Combined chlorine reacts much slower, making it unreliable for fast-moving industrial cooling or food processing lines.
Testing Complexity: DPD1 vs. DPD4
DPD1 tests exclusively for Free Chlorine.
DPD4 (or DPD3 + DPD1) tests for Total Chlorine. Subtracting the two gives you the Combined Chlorine level—a vital metric for indoor pools and wastewater plants.
EPA rules must be followed.
The EPA controls the amount of free chlorine in drinking water to make sure it is safe, and other environmental agencies keep an eye on the chlorine levels in trash to keep aquatic life safe.
Application Guide: Which One Should You Monitor?
| Application | Recommended Metric | Why? |
| Drinking Water & Food Processing | Free Chlorine | Ensures immediate disinfection and safety for consumption. |
| Swimming Pools & Spas | Both (Free & Total) | Essential to calculate combined chlorine to prevent eye irritation. |
| Wastewater Treatment | Total Chlorine | Required for legal compliance to ensure no toxic chlorine is discharged. |
| Cooling Towers | Free Chlorine | Prevents biofilm and Legionella while minimizing pipe corrosion. |

How to Fix a Chlorine Imbalance
The Science of Breakpoint Chlorination
To eliminate Combined Chlorine (the “smell”), you can’t just add a little more chlorine. You must reach the Breakpoint. This occurs when you add enough Free Chlorine (usually 10x the amount of Combined Chlorine) to fully oxidize the chloramines. Once the “waste” is burned off, your Free Chlorine levels will finally begin to rise steadily.
If your tests show high Combined Chlorine (the “smell”) and low Free Chlorine:
First, check the pH: Make sure your pH is between 7.2 and 7.6. Check your sensors with our [How to Calibrate pH Meter Guide].
Calculate the Gap: Subtract FC from TC to find your CC level.
Shock the Pool: Add a lot of chlorine (breakpoint chlorination) to “burn off” the Combined Chlorine.
Install a Continuous Sensor: Use a [Sino-Inst Residual Chlorine System] to keep the Free Chlorine level at 2.0 ppm all the time to stop further spikes.
The Invisible Link: Why pH Levels Rule Your Chlorine Efficiency
The Invisible Link: Why pH Levels Rule Your Chlorine Efficiency
Most people treat pH and Chlorine as two separate numbers, but in reality, they are inseparable. Chlorine’s ability to kill bacteria depends entirely on the acidity of your water. When you add chlorine to water, it forms Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl)—the active form that does the actual sanitizing.
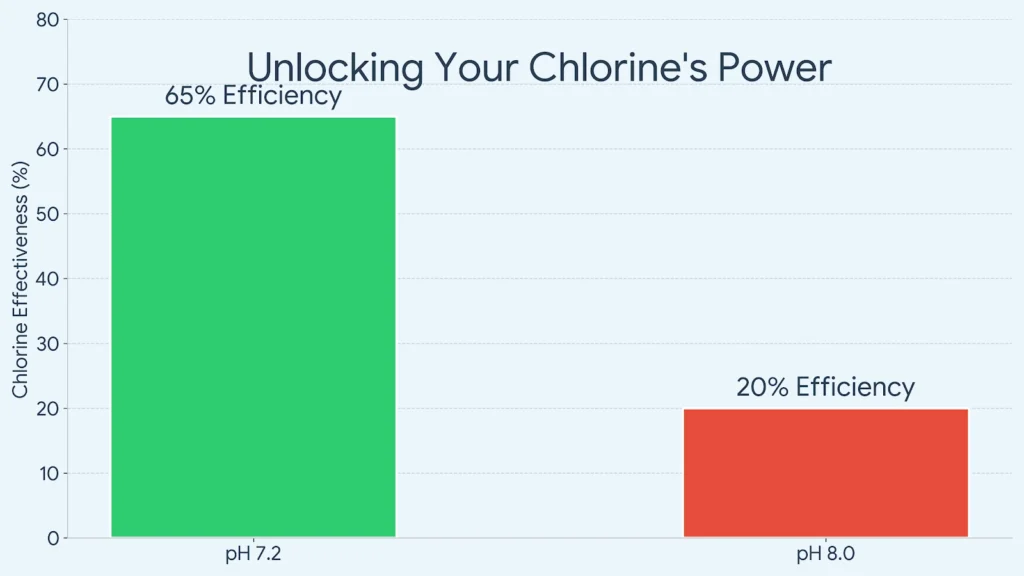
The Shocking Truth about pH:
- At pH 7.2: Your chlorine is highly active, with about 65% to 70% sanitizing power.
- At pH 8.0: Your chlorine’s effectiveness plummets to less than 20%.
The Conclusion: If your pH is too high, you can double your chlorine dosage and still have unsafe water. This is why we always recommend testing and calibrating your pH sensors before adjusting your chlorine. To eliminate this complexity, many professionals switch to a [Sino-Inst Dual pH & Chlorine Monitoring System], which tracks both parameters simultaneously to ensure your chemicals are always working at peak performance.
Summary: Mastering the Chlorine Balance
Managing your pool or industrial water system isn’t about how much chlorine you pour into the water—it’s about how much of that chlorine is active and effective.
- Free Chlorine is your defense system; keep it between 1.0 – 3.0 ppm.
- Combined Chlorine is a byproduct of contamination; keep it below 0.2 ppm to avoid odors and irritation.
- Total Chlorine is only a reference point; never rely on it alone to judge water safety.
By maintaining a proper pH balance and understanding the relationship between these three values, you can prevent algae growth, protect your equipment from corrosion, and ensure a safe environment for every user.
FAQ
Related Products
Online residual chlorine controller
Online residual chlorine electrode
Sino-Inst makes it easier to deal with difficult chemistry. We offer [High-Precision Residual Chlorine Sensors] and automated monitoring systems that give you digital accuracy to the 0.01 level in real time. Whether you run a high-end commercial pool or an industrial cooling tower, our technology makes sure that your Free Chlorine is always performing at its optimum.
Stop having to deal with water that is cloudy and smells like chemicals. Make decisions based on data and protect your investment for the long term.
Request A Quote
More Resources
-
Does Water Conduct Electricity? The Complete Science Guide (2026)
If you have ever been curious about ‘does water conduct electricity?’? )You are not alone. This is one of the most common questions…
-
The Definitive Guide to the Mass Flow Controller Working Principle
In industrial process control, achieving precise measurement and regulation of gas and liquid flows is an absolute necessity. Whether you are engineering a…
-
How to Get Rid of Chlorine in Water — The Complete Science-Backed Guide (2026)
If you’re searching for how to get rid of chlorine in water, you probably want better‑tasting tap water, healthier skin, or safe water…
-
Is It Safe to Drink Purified Water? Practical Guide to Making a Healthy Choice.
Is it safe to drink purified water? “Is the most crucial question for health conscious consumers when choosing bottled water or home water…
-
5 Kinds of Detector Detects Gas Leaks: Expert Selection Guide
In industrial safety, the margin for error is non-existent. Whether managing a petrochemical refinery, an agricultural greenhouse, or a manufacturing plant, the ability…
-
5 Expert Tips to Put an Explosive Gas Detector for Maximum Safety
Safety is not a variable; it is a constant requirement in industrial process control. When dealing with combustible gases, the difference between a…
.png)