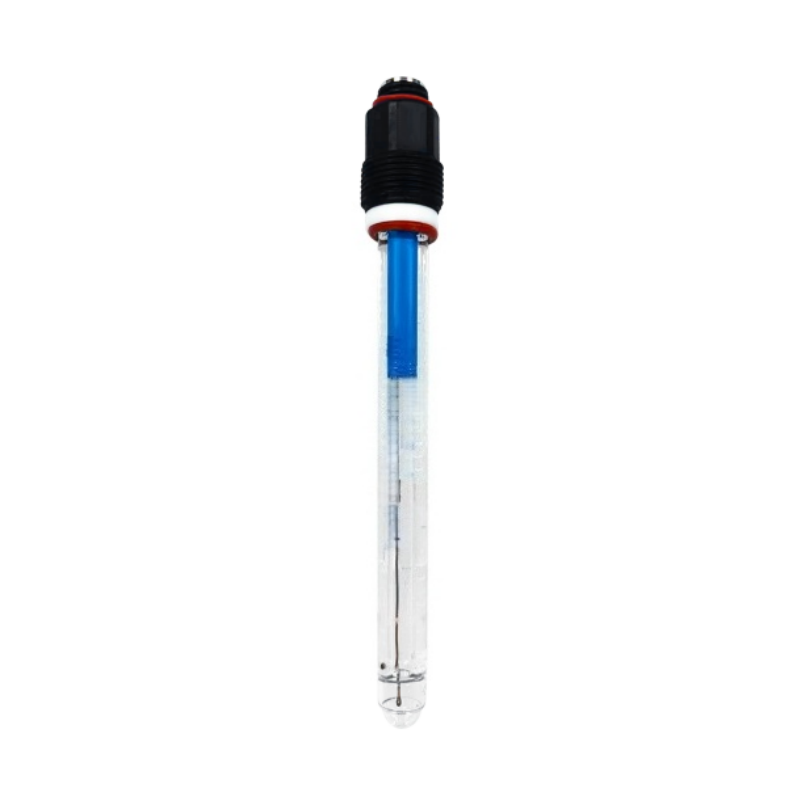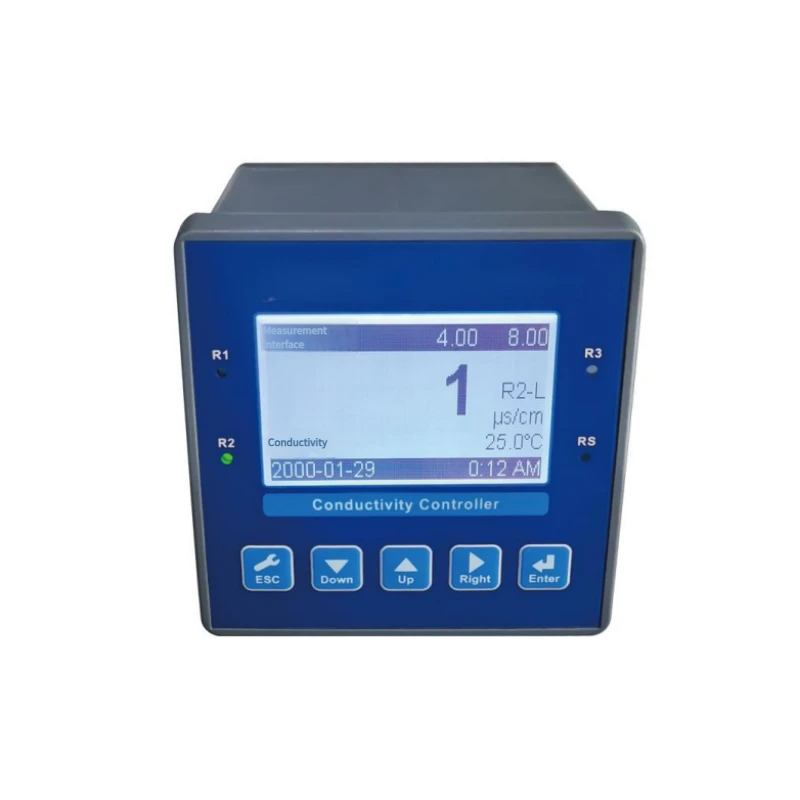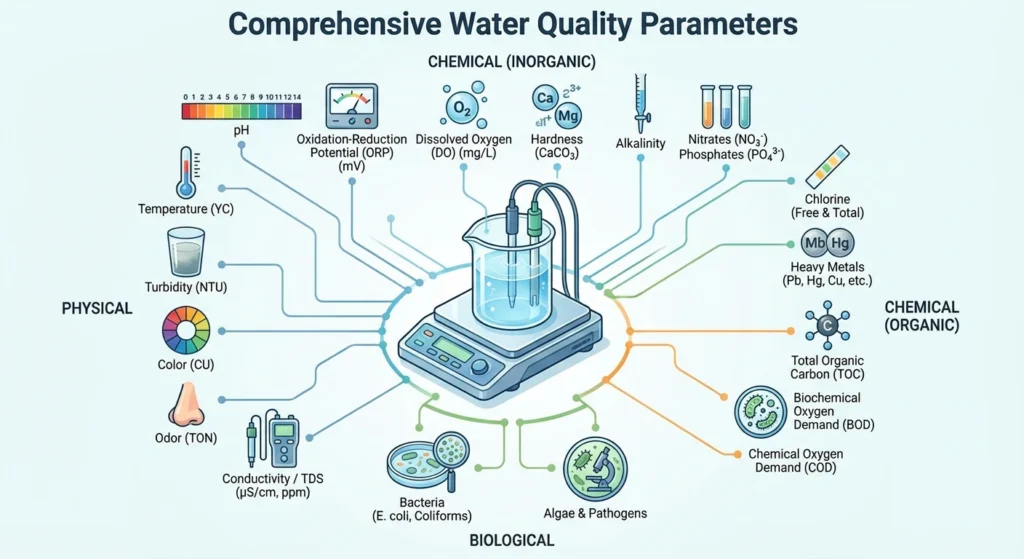
Water hardness is a measure of the amount of calcium and magnesium ions. It affects the cost of production, the safety of equipment operation, and the treatment of water. Too much hardness can cause scaling, blockage, and lower heat transfer efficiency in circulating water, boiler water, softened water, and reverse osmosis systems. Not enough hardness can affect the stability of the process and the quality of the water. Accurate, continuous, and real-time hardness monitoring is essential for the long life of equipment, the right dosage of medication, and the safe and effective operation of systems.
★★★★★
Product Preview
What is the water hardness?
The hardness of water mainly refers to the total concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in water, which is a core indicator for measuring the tendency of water quality to scale. It is usually expressed in mg/L (calculated as CaCO3) or ppm. The higher the hardness, the greater the risk of scaling in pipelines, heat exchangers, boilers, and membrane systems.

Why monitor water hardness?
- Stop scaling and clogging of pipes, heat exchangers, boilers, and reverse osmosis membranes.
- Keep equipment safe, make it last longer, and cut down on downtime for repairs.
- Control of softener function and scale inhibitor dosage is accurate, which saves money on chemicals.
- Make sure that drinking water, process water, and boiler feedwater are always safe and compliant.
- Make heat exchange more efficient, use less energy, and keep the system from becoming less efficient.
Core application scenarios
- Industrial circulating cooling water system: keeping an eye on hardness to stop heat exchangers and pipelines from scaling up and making sure heat transmission is as efficient as possible
- Water for the boiler and the softened water system: Monitoring the softening impact in real time to reduce the hazards of scaling and bursting pipes in the boiler
- A reverse osmosis (RO), nanofiltration, or ultrafiltration system checks the hardness of the water coming in to keep calcium and magnesium from building up on the membrane parts.
- Waterworks and drinking water treatment: keeping an eye on hardness indicators to make sure the safety of the water supply fulfills standards

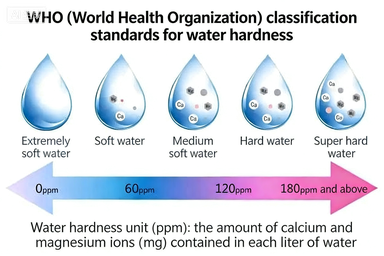
Water Hardness Classification Standards (as CaCO₃)
| Hardness Level | Concentration (mg/L) | Scaling Risk | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Soft Water | < 50 | None | Drinking water, ultrapure process water |
| Soft Water | 50 – 150 | Low | Tap water, general process water |
| Medium-Hard Water | 150 – 300 | Medium | Cooling water (minor anti-scaling required) |
| Hard Water | 300 – 450 | High | Untreated groundwater, industrial wastewater |
| Ultra-Hard Water | > 450 | Very High | High‑calcium/magnesium groundwater |
International Water Hardness Classification (USGS Standard)
| Classification | mg/L (as CaCO₃) |
|---|---|
| Soft | 0 – 60 |
| Moderately Hard | 61 – 120 |
| Hard | 121 – 180 |
| Very Hard | > 180 |
How to pick the right treatment procedure based on water hardness?
Water with varied levels of hardness has different risks of scaling and needs for treatment. To keep expenses down and make sure the treatment works, you need to choose the right plan based on the real hardness value.
Soft water (with low hardness) generally has a low risk of scaling, and can be stabilized by adding an appropriate amount of scale inhibitor. Combined with HR-100 online hardness monitoring, real-time monitoring of water quality changes can be achieved.
There is a clear tendency for scaling in medium hard water (with moderate hardness). It is recommended to use a combination of softening pretreatment and scale inhibitors, with a focus on monitoring the hardness of softened water to ensure that the water quality entering the system meets the standard.
The risk of scaling in hard/high hardness water is extremely high, and it is necessary to use powerful softening processes such as ion exchange softening, lime softening, reverse osmosis RO, etc., and achieve online continuous monitoring through HR-100 to avoid equipment scaling, blockage, and efficiency decline caused by excessive hardness.
Regardless of the processing method used, online hardness monitoring is an essential step.
Technical Support
Choosing a pH Meter for Water:The Professional Guide to(2026)
What Is Dissolved Oxygen in Water? The Ultimate Guide to Monitoring(2026)
The Shocking Truth About the pH of Distilled Water: Why It’s Not 7.0
Mastering Water Quality Parameters: Professional Guide To Control(2026)
How to Raise pH in Pool: The Chemical Guide & The Automated Solution
How to Calibrate pH Meter: A Step-by-Step Guide for Accurate Readings
Accurately monitoring the hardness of water quality is the fundamental work to ensure the stable operation of water treatment systems, prevent scaling risks, and improve operational efficiency. Sino Inst online hardness analyzer provides professional hardness online monitoring solutions for industrial and municipal users with stable and reliable performance, simple operation and maintenance, helping to achieve intelligent, automated and refined water quality management, and ensuring long-term safe and efficient operation of the system.
Request a Quote
.png)