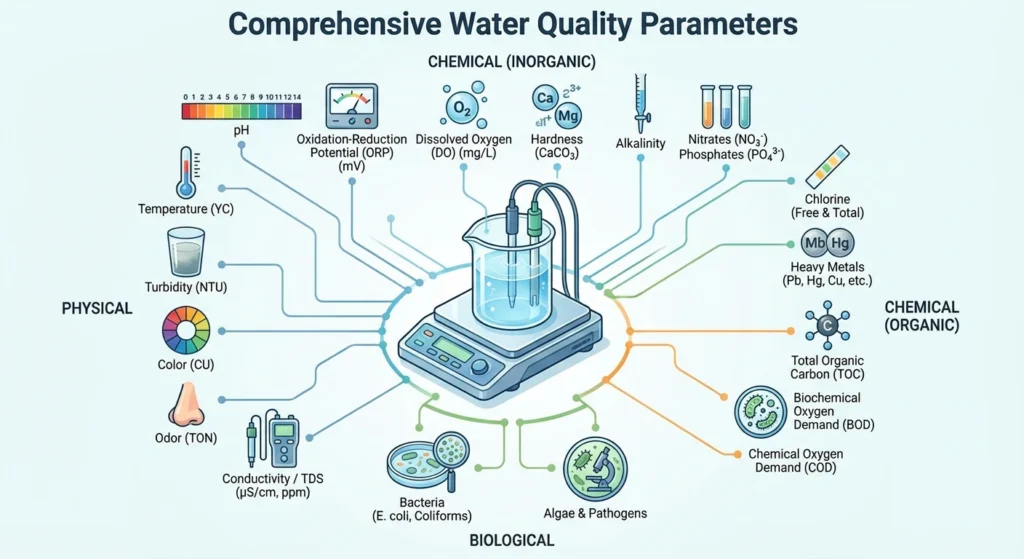
The drug concentration is a core key indicator for the operation and maintenance of industrial circulating water, water treatment and other systems. Accurate concentration monitoring and control directly determine the efficiency of system operation, equipment service life and the cost of chemical dosing. This section focuses on the core requirements of online monitoring of drug concentration and provides integrated monitoring solutions. Professional equipment is used to achieve real-time, accurate, and continuous monitoring of concentration, providing scientific data support for drug control in various industries’ water treatment systems.
★★★★★
Product Preview
What is drug concentration?
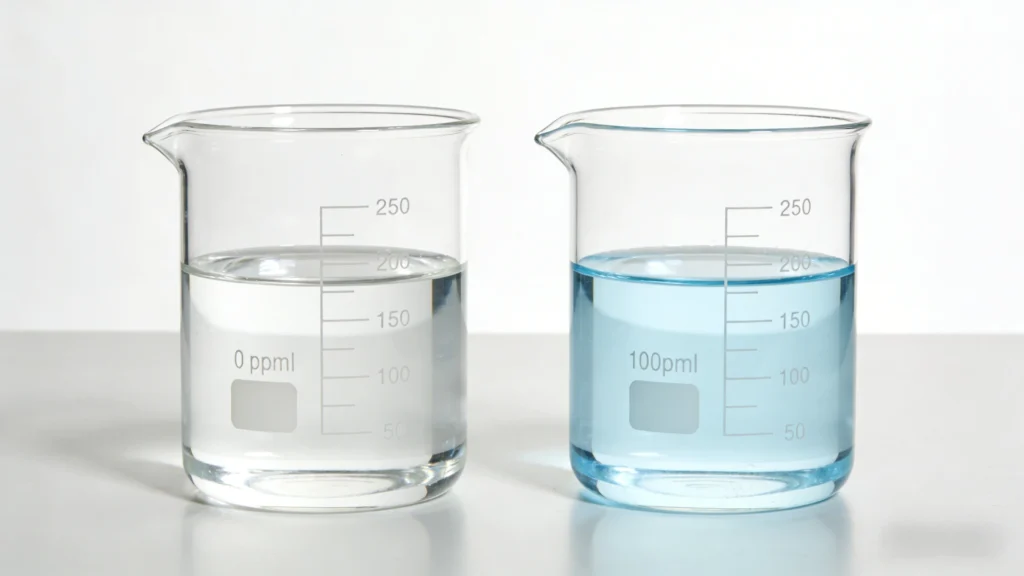
Drug concentration, in simple terms, refers to the effective content of water treatment agents in a certain volume/mass of water (or other medium). It is a core quantitative indicator for measuring the dosage of agents and controlling their effects in water treatment systems. The commonly used unit is ppm (parts per million, equivalent mg/L), and it is also one of the most critical operation and maintenance parameters in industrial circulating water, water treatment and other scenarios.

The core difference between drug concentration and “dosage”
Many people confuse the two, but they are fundamentally different:
Dosage of medication: refers to the total mass/volume of medication artificially added to the water body, which is the “input value”;
Drug concentration: refers to the actual amount of active ingredients retained in the water after the addition of the drug, which is the “actual value”.
Due to factors such as water impurity reactions, chemical degradation, and system overflow, the dosage does not equal the actual concentration. This is also why it is necessary to monitor the concentration of chemicals in real-time online, rather than relying solely on dosage estimation.
Simple understanding: The dosage is “how much medicine we have added”, and the concentration of the medicine is “how much medicine can actually work in the water”. Monitoring the concentration of the medicine is to accurately match the “actual demand” of the “dosage” and achieve efficient, energy-saving, and compliant water treatment.
Core application scenarios
- Power industry: Circulating cooling water system for thermal power plants/hydropower stations (monitoring of corrosion and scale inhibitors, fungicides concentration)
- Chemical industry: Process circulating water, cooling water pipe network (concentration control of various water treatment agents)
- Water supply/sewage treatment industry: water purification and reclaimed water reuse system (monitoring of flocculant and disinfectant concentration)
- Pharmaceutical/Food Industry: Sanitary grade circulating water in production workshops (controlled concentration of chemicals that meet process standards)
- Metallurgical/paper industry: Industrial circulating water system (monitoring of anti-corrosion and anti scaling agent concentration)

Why do we need to test the concentration of drugs?
- Ensure the efficacy of the medication and ensure the effective performance of corrosion inhibition, scale inhibition, sterilization and other functions
- Avoid insufficient concentration, prevent equipment and pipeline corrosion, scaling, and bacterial and algal growth that may cause malfunctions
- Prevent excessive medication, reduce material waste, and lower production and operational costs
- Control water quality to meet standards and meet the requirements of water treatment processes and hygiene standards in various industries
- Realize precise dosing to match the actual working conditions with the dosage of the medication
- Ensure system stability and improve overall operational efficiency of the circulating water/water treatment system
Characteristics of drug concentration in different scenarios
Industrial circulating water system
The 350A value (0-99.9ppm) and TP value (0-9.99ppm) are commonly used to characterize the effective concentration of tracer/agent, and the concentration is required to be kept within the process threshold range: too low can not play the role of corrosion inhibition, scale inhibition and sterilization, too high will cause waste of agent, and may also cause secondary problems such as scaling and foam in water bodies.
Water purification/sewage treatment
The concentration of coagulants and disinfectants needs to be adjusted in real-time to match the water quality and quantity. For example, if the concentration of disinfectants is too low to achieve sterilization effect, and too high, harmful substances will remain, violating water quality standards.
Technical Support
Choosing a pH Meter for Water:The Professional Guide to(2026)
What Is Dissolved Oxygen in Water? The Ultimate Guide to Monitoring(2026)
The Shocking Truth About the pH of Distilled Water: Why It’s Not 7.0
Mastering Water Quality Parameters: Professional Guide To Control(2026)
How to Raise pH in Pool: The Chemical Guide & The Automated Solution
How to Calibrate pH Meter: A Step-by-Step Guide for Accurate Readings
For water treatment systems to perform efficiently, steadily, and at a low cost, they need to be able to accurately and in real time track the concentration of reagents. A solid concentration control system not only makes sure that sterilization, corrosion, scale, and water purification operate, but it also saves down on chemical waste, extends the life of equipment, and helps organizations manage their operations in a sensible and consistent way.
Request a Quote
.png)