Is distilled water the same as purified water? Most people answer “Yes” because both look crystal clear. But in the world of high-precision chemistry and industrial maintenance, that “Yes” could be a costly mistake.
At Sino-Inst, we’ve seen countless sensors fouled and cooling systems corroded simply because the operator didn’t understand the invisible chemical differences between these two fluids. While they may look identical in a glass, their conductivity, pH stability, and aggressive nature are worlds apart.
If you are using the wrong water for your laboratory experiments, industrial chillers, or even high-end appliances, you aren’t just losing efficiency—you’re risking your equipment.

Distilled and purified water?
What is distilled water
Definition: Water of very high purity that is made by heating, boiling, evaporating, and then condensing and recovering. This technique mimics and accurately manages the natural water cycle. Its goal is to get rid of practically all dissolved minerals, inorganic salts, microbes, and most non-volatile pollutants from water.
What is purified water
Definition:Pure water is water that has been through a number of physical and chemical processes to get rid of harmful chemicals, contaminants, and bacteria and meet certain purity standards, usually those for safe drinking. This group’s main goal is to make water that is safe and tastes good.
One sentence comparison and summary
- Distilled water is a special type of water that pursues ultimate chemical purity through “phase transition”.
- Purified water is a universal commodity water that meets safe and delicious standards through “filtration”.

Applications for Purified Water
- Drinking Water: People often choose it since it tastes better and is still safe.Pharmaceutical Production: Used to make a lot of medicines and for cleaning.
- Food and drink: water as an ingredient to make sure the quality of the product stays the same.
- Industrial Cooling: Stops scale from building up in big chillers and boilers.
Uses for Distilled water
- Laboratory Reagents: Necessary for delicate investigations where mineral contamination must be eliminated.
- Medical devices like CPAP machines, autoclaves, and humidifiers use this to stop mineral buildup.
- Car batteries and steam irons: stops scale and rust, which makes the equipment last longer.
- Certain industrial processes demand the complete absence of minerals, even if it costs more.
Distilled vs. Purified Water
Click on either title below to expand and view its detailed pros and cons.
Pros & Cons of Distilled Water
Advantages
- Very Pure:There are almost no minerals, salts, or microorganisms in it.
- Consistent Baseline: Ideal for experiments where variable minerals would skew results.
- Prevents Scale: Extends the life of appliances like steam irons and humidifiers.
- Industry Standard: Required for medical devices (e.g., CPAP) and automotive batteries.
Disadvantages
- Flat Taste: Lacks minerals, making it taste bland for drinking.
- Energy Intensive: The distillation process consumes significant energy.
- May Retain VOCs: Some volatile organic compounds can evaporate and re-condense with the water.
- Removes Beneficial Minerals: Not ideal for daily consumption as it lacks calcium and magnesium.
Pros & Cons of Purified Water
Advantages
- Safe & Great-Tasting: Removes contaminants while often keeping a balanced mineral profile.
- Cost-Effective: Methods like reverse osmosis are efficient for large-scale production.
- Highly Versatile: Suitable for drinking, cooking, pharmaceuticals, and most industrial uses.
- Broad-Spectrum Removal: Effective against chemicals, microbes, and heavy metals.
Disadvantages
- Varying Standards: “Purified” is a broad term; purity depends on the specific filtration method.
- Potential Mineral Loss: Some methods (e.g., RO) remove most minerals, which may require re-mineralization.
- Not Absolute: Filter quality varies; some may not remove all pharmaceutical residues.
- Wastewater Generation: Processes like RO can produce significant wastewater.
5 Critical Differences: Why It Matters for Your Business
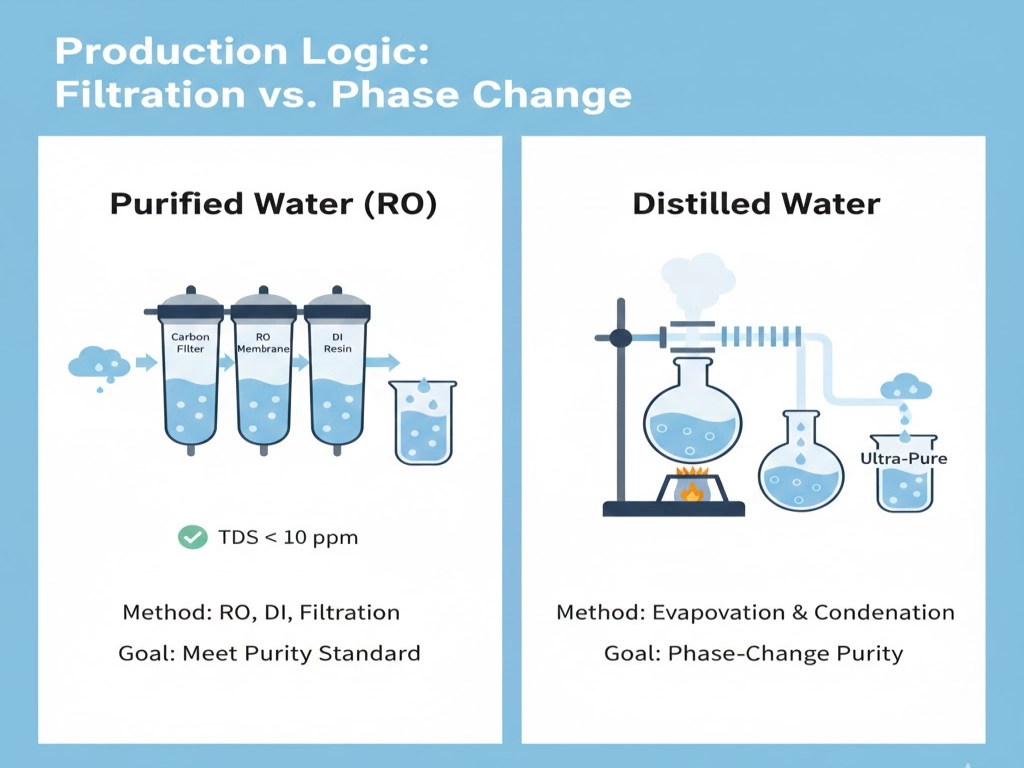
Production Logic: Filtration vs. Phase Change
When asking is distilled water the same as purified water, you must first look at their origin.
- Purified Water is an “evolution” of tap water, using Reverse Osmosis (RO) or carbon filters to strip impurities to below 10 ppm.
- Distilled Water is a “rebirth.” Water is boiled into steam—leaving minerals and heavy metals behind—and then condensed back into a liquid.
The Verdict: Distillation is superior at removing viruses and minerals, but RO (Purified) is more energy-efficient for large-scale production.
Conductivity: The “Ghost” in the Liquid
This is the most critical technical difference for engineers and lab technicians.
- Purified water (RO/DI): Typically has a conductivity of 5–10 μS/cm. While clean, it still contains trace ions.
- Distilled water: Can achieve a staggering < 1 μS/cm. It is a near-perfect insulator.
The Verdict: For cooling semiconductors or electronics, distilled water is the best choice for zero-conductivity needs.
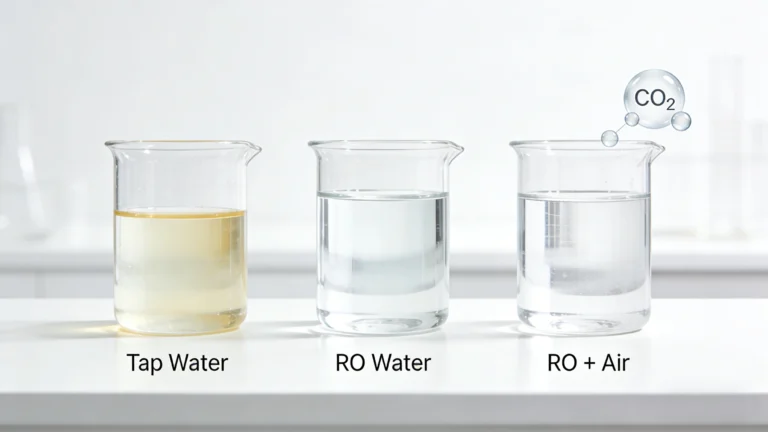
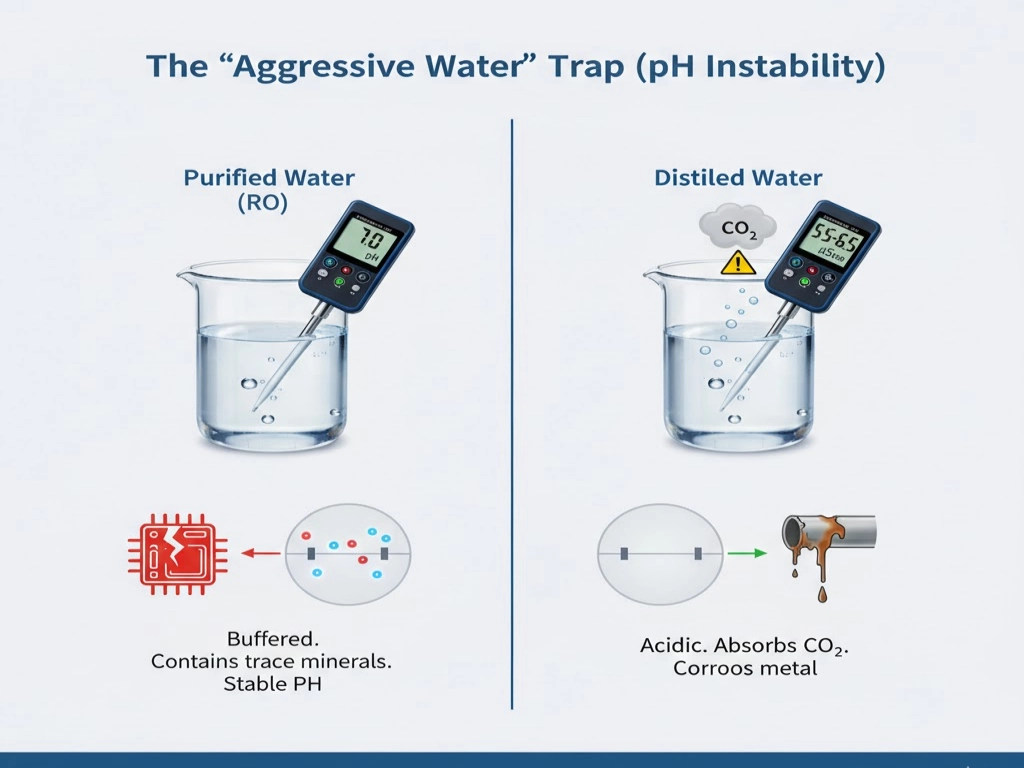
The “Aggressive Water” Trap (pH Instability)
Did you know distilled water is “hungry”? Because it lacks minerals, it is chemically unstable. The moment it touches air, it absorbs CO₂ and drops to a pH of 5.5–6.5.This acidic “aggressive water” can slowly corrode copper pipes and metal valves—a hidden risk purified water typically avoids.
Maintenance and Operational Cost
Budget often dictates the choice between these two:
- Purified (RO) Systems: Higher cost in filters and membranes, but highly energy-efficient for high-volume industrial use.
- Distilled Units: Extremely high energy (electricity) demand. Minerals “bake” onto heating coils, requiring frequent descaling.
The Verdict: For large-scale production, RO is the financial winner; for small-batch precision, distillation is worth the cost.
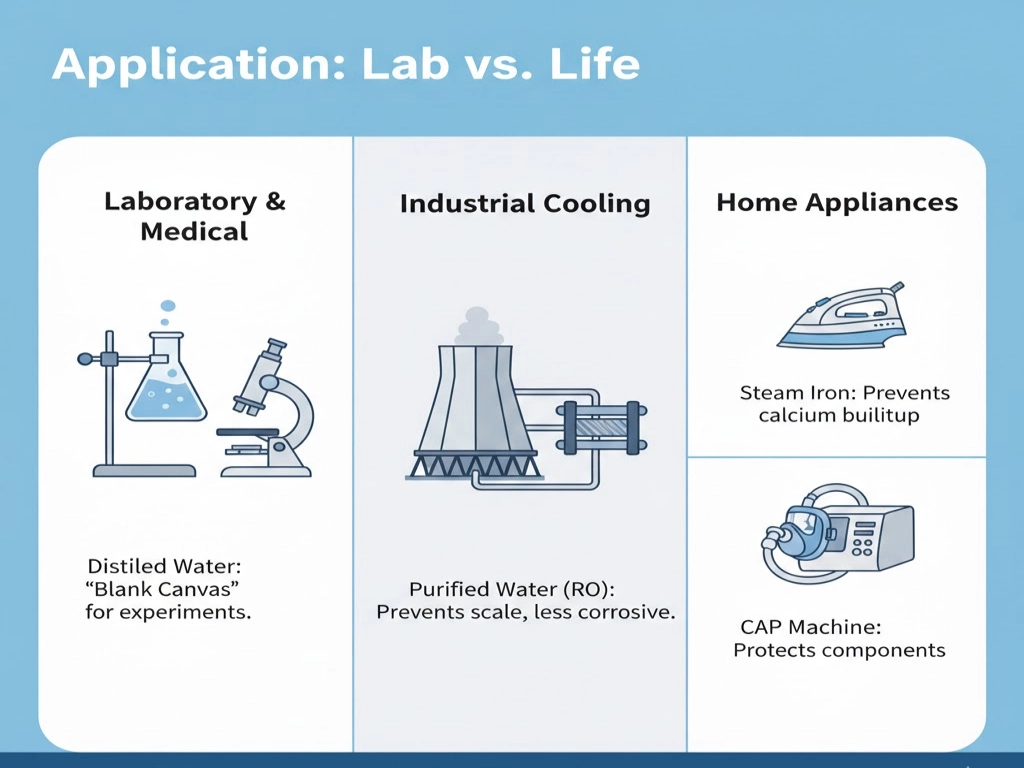
Application: Lab vs. Life
Where you use the water determines your choice:
- Laboratory & Medical: Distilled water is the “blank canvas.” It won’t interfere with delicate chemical reactions.
- Industrial Cooling: Purified (RO) water is preferred as it is less “aggressive” toward metal infrastructure while still preventing scale.
- Home Appliances: Distilled is best for steam irons and CPAP machines to prevent calcium buildup.
How to choose distilled water or purified water?
| Use Case | Recommended Choice | Reasons | Expert Advice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Household Drinking / Cooking | Purified Water | Filters pollutants while retaining trace minerals, offering a more natural taste. | Suitable for long-term daily consumption. |
| Precision Laboratory (High Requirements) | Distilled Water | Near-zero conductivity, eliminates ionic interference, and ensures experimental consistency. | Must monitor pH changes caused by CO₂ absorption. |
| CPAP Machine / Humidifier | Distilled Water | Completely scale-free, protecting the machine’s precision heating wires and ultrasonic components. | Prevent the formation of “white powder” deposits. |
| Lead-Acid Battery / Iron Maintenance | Distilled Water | Extremely pure, preventing mineral deposition on electrode plates that can cause short circuits. | The best investment to extend equipment lifespan. |
| Industrial Large-Scale Cooling Circuits | Purified Water | Low production cost (RO process), sufficient to prevent large-scale scaling. | It is recommended to install an online conductivity meter for real-time monitoring. |
| Pharmaceutical / Vaccine Production | Injectable-Grade Distilled Water | Absolute control of pyrogens and microorganisms. | Complies with strict pharmacopoeial standards. |
Conclusion: The Final Word on Purified Water and Distilled Water
Returning to the original question: Is distilled water the same as purified water?
From a legal and labeling point of view, distilled water is a type of pure water. But when it comes to technology and use, the answer is a clear “no.” Their subtle differences in mineral content, conductivity, pH stability, and production costs determine their different fates in laboratories, factories, and households.
Core points review:
- Distilled water is the preferred choice for pursuing “zero minerals” and is most suitable for precision instruments, laboratory analysis, and preventing scale buildup.
- Purified water is the first choice for pursuing “efficiency and cost-effectiveness”, and is most suitable for large-scale industrial cooling, pharmaceutical basic water, and daily drinking.
Expert’s final suggestion
No matter which type of water you choose, its purity cannot be determined by the naked eye.In industrial procedures, even 0.1 milligrams of leftover contaminants can cause the whole batch of items to be thrown away or sensors to break down.
As a leader in the field of process monitoring, Sino Inst suggests not relying on the name of the water source, but on real-time monitoring data. By installing high-precision online conductivity meters and low conductivity pH sensors, you can ensure that your ‘purified water’ always stays within the required standards.
FAQ
Related Products
Answering the initial question: Is distilled water the same as purified water? This difference may seem insignificant, but in high-precision businesses and rigorous labs, it can effect the longevity of your tens-of-thousands-of-yuan equipment, production stability, and experimental outcomes. Purity should be a specific, real-time number, not just a label.
Sino-Inst (China Instrumentation Electronics) is the best water quality protection for distilled or purified water. After years of industrial water quality monitoring experience, we offer high-precision online conductivity meters, low-conductivity-specific pH sensors, and integrated water quality monitoring systems to thousands of pharmaceutical, power, and chemical companies globally.
Request A Quote
More Resources
-
The 10 Best Digital carbon monoxide detectors 2026: An Industrial Guide
Carbon monoxide (CO) remains one of the most hazardous invisible threats in industrial, commercial, and residential environments. Colorless, odorless, and tasteless, it requires…
-
Can gas detectors detect multiple gases simultaneously?
In the complex and often hazardous world of industrial manufacturing, petrochemical processing, and confined space operations, ensuring the safety of personnel is the…
-
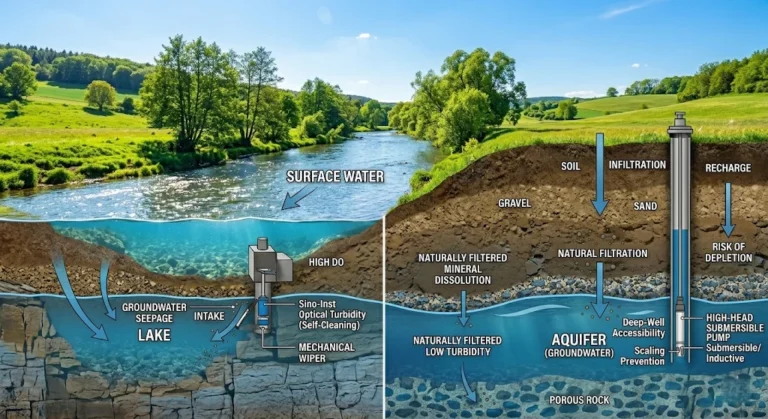
Surface Water vs Groundwater: A Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality
In the domains of environmental engineering and industrial water management, knowing the basic differences between surface water vs groundwater is not just an academic…
-
What is the pH of Reverse Osmosis Water? The Complete Science Guide (2026)
If you have ever been curious about ‘what is the pH of reverse osmosis water?’, you are not alone. This is one of…
-
The Top 8 Portable CO Detector for Car Use
Introduction: The Silent Threat in Automotive Cabins Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas generated by the incomplete combustion…
-
6 Best Mass Flow Controller for Liquids: An Expert Technology Guide
In modern industrial automation, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor fabrication, the precise control of fluid dynamics is a fundamental requirement. Relying on outdated volumetric…
.png)