Pool maintenance often focuses our attention on pH and chlorine content, but there is an often overlooked indicator – Total Alkalinity (TA) – which is the “invisible cornerstone” that truly determines water quality stability.
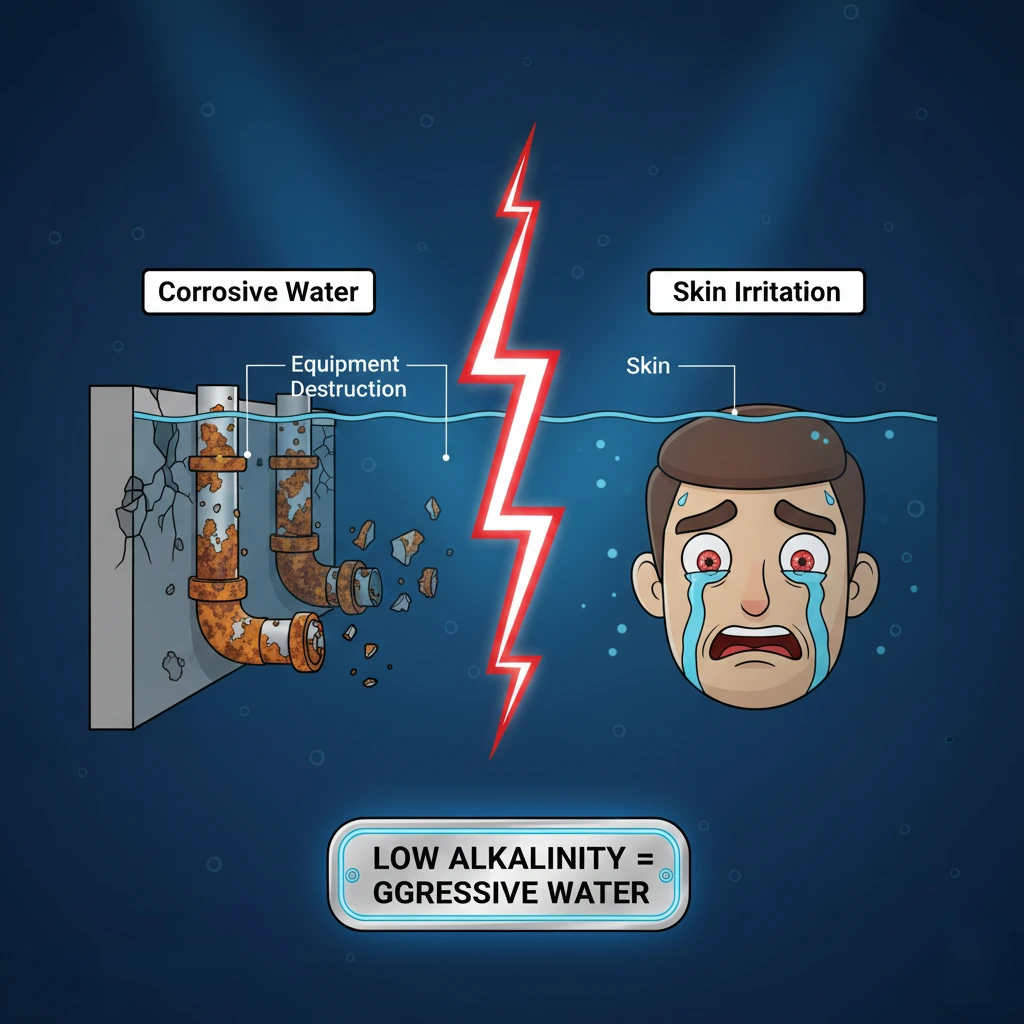
When you notice low alkalinity in the pool, it acts like an ‘invisible killer’ silently destroying your expensive equipment. Low alkalinity not only causes drastic fluctuations in pH value, but also corrodes pool walls and pipelines, making your maintenance work twice as difficult and costly..
This blog will take you to a deeper understanding of all the potential hazards of alkalinity low in pool, providing you with a more precise and comprehensive solution than traditional methods, and revealing the “behind the scenes” behind the repeated occurrence of alkalinity problems.

Alkalinity and Water Quality
Definition: Total alkalinity is an indicator of the “acid buffering capacity” of water. It is like a shield, protecting the pH value from being easily shattered by acidic substances such as acid rain, sweat, and pesticides.
The core relationship between alkalinity and water quality:
- PH stabilizer: Suitable alkalinity (80-120 ppm): The pH value is stable, like a car with brakes.
- Low alkalinity (<80 ppm): produces “pH bounce”, with pH values fluctuating up and down, completely uncontrollable.
Physical disruption (LSI equilibrium):
Low alkalinity=corrosiveness: Water will directly corrode the copper pipes of the heater, water pump, and pool wall plaster in order to find balance.
High alkalinity=scaling: Mineral precipitation in water leads to turbidity and the formation of hard scale on pipelines and pool walls.
Cost impact: Stable alkalinity can protect the activity of chlorine, prevent chemical failure, and save about 30% -50% of chemical maintenance costs.
Is low alkalinity in pool dangerous?
Dangerous and “slow and expensive”.
This is shown in three areas:
- Health risks: Low alkalinity immediately lowers pH to below 7.0. Acidic water can strip skin and hair of oil, causing eye irritation, itching, and chlorine to be less effective, promoting bacterial development.
- Low-alkalinity water corrodes equipment. To discover mineral balance, it will immediately erode the heat exchanger’s copper pipes (causing water leaks) and the water pump’s metal parts from the inside, incurring thousands of dollars in equipment damage.
- The plaster layer or tile joints on the pool wall “suck” calcium, damaging the pool body. This will make the pool surface rough and cracked like sandpaper, cutting swimmers’ feet and allowing black algae to colonize.
How to Diagnose if Alkalinity Low in Pool?
Accurate diagnosis is crucial before taking any action.
- Indicator definition: The ideal range for total alkalinity in a swimming pool is usually between 80-120 ppm (parts per million). Below 80 ppm means your pool is in a low alkalinity state.
- List of common symptoms:
- The pH value is difficult to stabilize: this is the most obvious signal. You may have just adjusted the pH, but soon it changed again.
- Poor chlorine disinfection effect: Even with sufficient chlorine added, the water quality remains turbid or algae appear.
- The water quality is green: there are repeated algae problems, and the effectiveness of algae removal agents is poor.
- There are signs of corrosion on the pool walls and equipment: metal parts rust, and the plaster layer on the pool walls peels off or becomes rough.
- Eye and skin discomfort: Swimmers complain of red eyes and itchy skin.
💡 Say goodbye to ‘blind guessing’, you need more precise tools Traditional colorimetric test strips have significant visual errors when facing pH Bounce, making it difficult to capture the true pH fluctuations.
Sino-Inst’s High precision digital pH meter is designed to solve this problem. It can provide real-time and accurate readings at the 0.01 level, allowing you to seize the opportunity before acidic corrosion occurs. Instead of worrying about the color of the test paper, it’s better to use numbers to provide authoritative basis for alkalinity adjustment and protect expensive equipment from damage.
Practical Guide: Precise Control of Alkalinity Low in Pool
When alkalinity low in the pool is detected, blindly dumping chemicals will only lead to turbid water quality. What you need is “Precision Strike” :
Core ingredient: Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda)
The only professional choice for increasing alkalinity. Do not use soda ash unless you want the pH value to get out of control.
Exclusive precise investment method (missing content from competitors):
Staged “Step by Step Addition”: Principle: Never add more than 50% of the total demand at once.
Reason: Alkalinity regulation has hysteresis. Adding too quickly at once can cause a momentary imbalance in calcium balance, leading to a “white cloud like” turbidity.
The “3-6-24” rule:
After adding, the pump circulates for 3 hours; Initial test after 6 hours; Final test will be conducted 24 hours later. Only readings after 24 hours are stable.
Avoid ‘local dead corners’:
Slowly sprinkle in front of the return water outlet and quickly dilute with strong water flow. It is strictly prohibited to directly pour into the skimmer, as this can damage the filter medium.
Accurate calculation reference:
Goal: Increase TA of 10000 gallons of water by 10 ppm.
Dosage: Approximately 1.5 lbs (0.68 kg) of sodium bicarbonate.
In my years of working with industrial water sensors, I’ve seen pool owners waste hundreds of dollars on pH-Up chemicals, only to realize the root cause was always the total alkalinity being off by a few ppm.

What causes high or low alkalinity?
| Direction | Cause | Why it happens |
| LOW ALKALINITY📉 | Trichlor Tabs | Strong acidity continuously consumes TA. |
| LOW ALKALINITY📉 | Acid Rain | Natural acidity neutralizes the water “shield.” |
| LOW ALKALINITY📉 | Over-Acidifying | Adding too much pH Down drops TA as well. |
| LOW ALKALINITY📉 | Soft Water | Topping off with low-mineral tap water. |
| HIGH ALKALINITY📈 | Hard Water | Source water is naturally rich in bicarbonates. |
| HIGH ALKALINITY📈 | Liquid Chlorine | High-pH sanitizers slowly push TA upward. |
| HIGH ALKALINITY📈 | Evaporation | Water leaves, but alkaline minerals stay & concentrate. |
| HIGH ALKALINITY📈 | New Plaster | New pool surfaces leach alkaline material as they cure. |
When your total alkalinity is below 80 ppm, the pool water loses its buffering capacity. At this point, the so-called ‘pH Bounce’ phenomenon occurs – any small external disturbance (such as a few rains, or even a bucket of chlorine solution) will cause your pH value to oscillate violently between the acidic and alkaline ends, making it impossible for you to stabilize it in the ideal range of 7.4-7.6.
Traditional weekly manual testing is simply unable to cope with this uncontrollable pH Bounce. You need a high-precision pH meter (or online controller) from Sino-Inst, which captures every small jump through 24/7 real-time monitoring and provides early warning before acidic corrosion actually occurs.
Conclusion: Mastering Alkalinity and Swimming Pool Health
Total alkalinity is a crucial aspect of swimming pool water quality management. By understanding its function, learning the correct detection and adjustment methods, and adopting long-term maintenance strategies, you will be able to bid farewell to the troubles of pH fluctuations and equipment corrosion, and truly enjoy clear, comfortable, and healthy swimming pool time.
Remember, pool management is not an isolated adjustment of indicators, but a collaborative balance of all water quality parameters. Starting today, give due attention to total alkalinity!
.png)