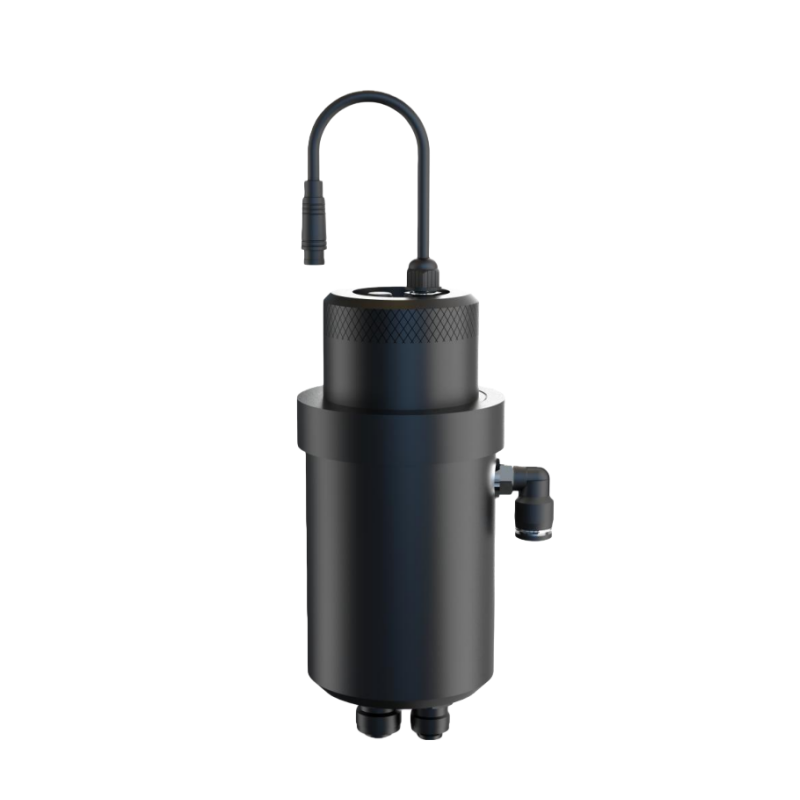
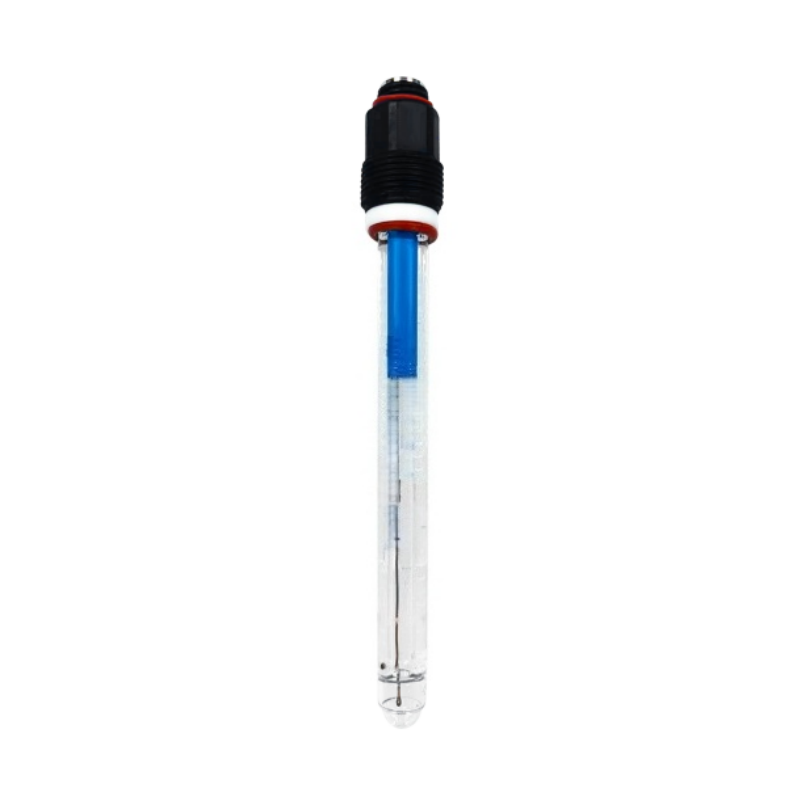
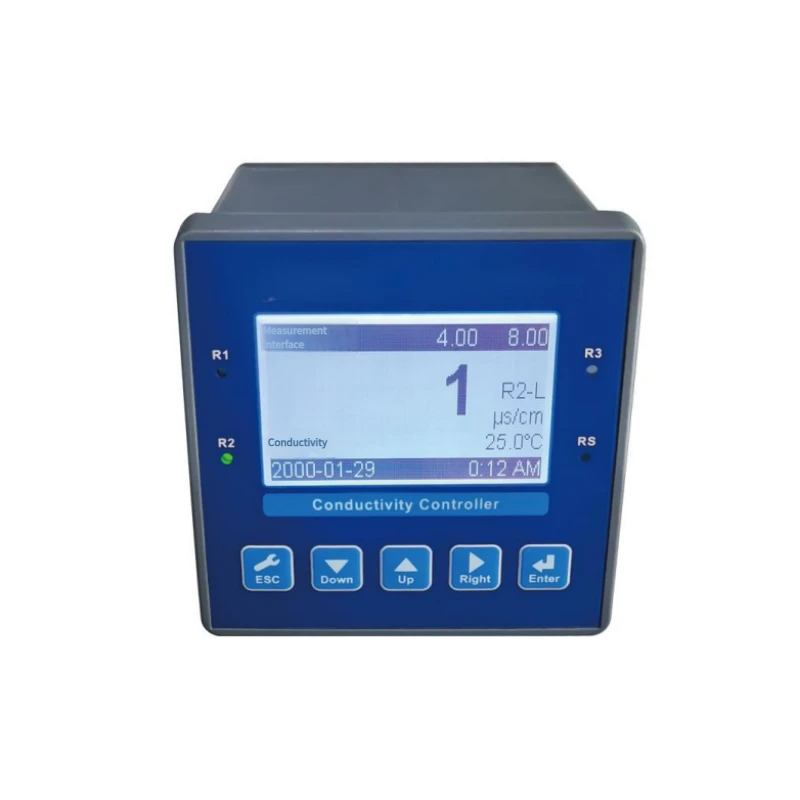
Turbidity, suspended solids (SS), and sludge concentration (MLSS) in water quality are core indicators that reflect the cleanliness, pollution level, and biochemical treatment efficiency of water bodies. Their precise monitoring is directly related to water supply safety, environmental compliance, and process optimization.
Real time tracking and data analysis of three types of indicators, from water purification in water plants to standard discharge in sewage treatment plants, from industrial production of circulating water control to ecological protection of surface water, are key links in ensuring water quality safety, reducing operating costs, and protecting the ecological environment. This interface integrates full scenario monitoring products and core knowledge to provide professional and efficient solutions for different needs.
★★★★★
Quick product navigation
Online turbidity/SS/MLSS controller
Clarity on key terms
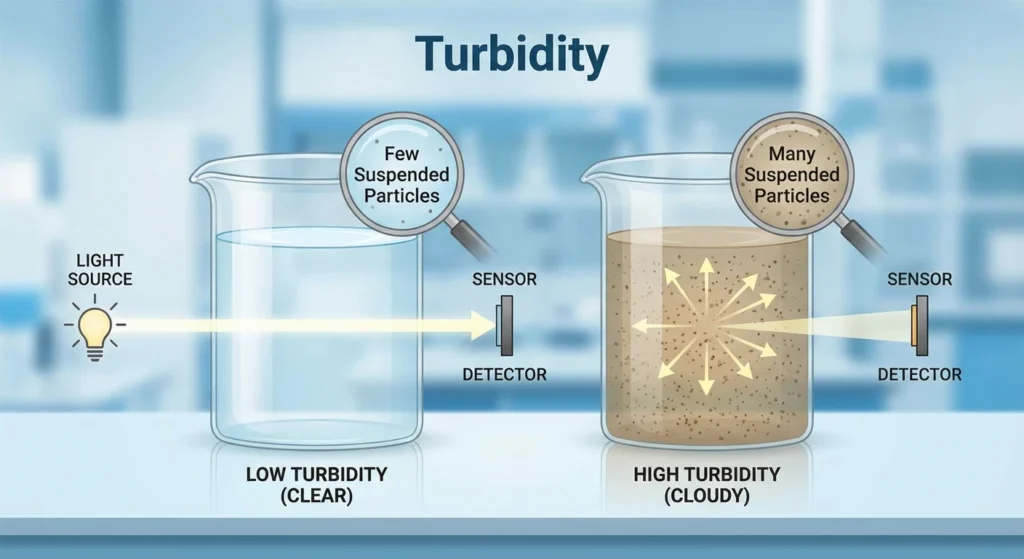
Turbidity
Water turbidity, expressed in NTU, is caused by suspended particle materials (bacteria, organic matter, silt, etc.). Turbidity affects aquatic life and disinfectant effectiveness while indicating the purity of the water.It is essential for drinking water and surface water safety assessment.
Sludge concentration
SS refers to solid particles suspended in water (0.1 μ m-1mm in size), measured in mg/L, such as inorganic sediment, organic detritus, and colloidal particles. Its content is closely related to water body transparency and pollution load and is the main control indicator for industrial and domestic sewage discharge compliance.
MLSS sludge concentration
The dry weight concentration of activated sludge in the sewage treatment biochemical system, measured in mg/L, indicates microbial number and activity. Its numerical value directly impacts biochemical reaction efficiency, aeration energy consumption, and effluent quality, and is a significant sewage treatment plant process parameter.
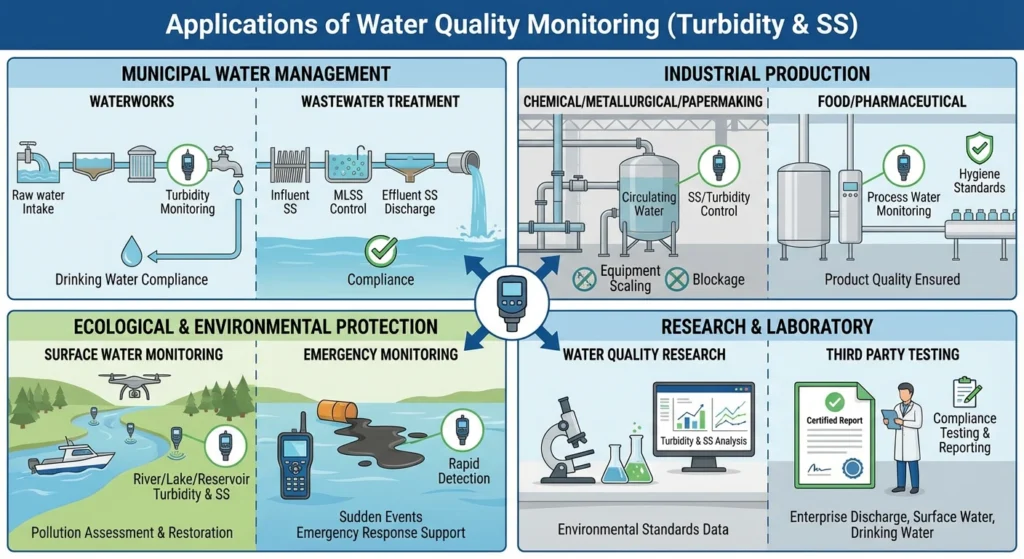
Applications
Municipal water management field
Waterworks: raw water turbidity monitoring, sedimentation tank/filter effluent turbidity control, ensuring the supply of drinking water meets the standard;
Wastewater treatment plant: Screening of influent SS concentration, real-time control of MLSS in the biochemical tank, monitoring of effluent SS discharge from the secondary sedimentation tank to ensure compliance with treatment requirements.
Industrial production field
Chemical/metallurgical/papermaking: SS pre-treatment monitoring of production wastewater, turbidity control of circulating water, to avoid equipment scaling and pipeline blockage;
Food/Pharmaceutical: Monitor the turbidity of process water, meet the hygiene standards for production water, and ensure product quality.
Ecological and environmental protection field
Surface water monitoring: tracking turbidity and SS concentration of rivers, lakes and reservoirs to assess water pollution status and ecological restoration effect;
Emergency monitoring: Rapid detection of turbidity/SS at the site of sudden water pollution events (such as sediment loss and illegal discharge of wastewater) to provide data support for emergency response.
Research and laboratory fields
Water quality research: analysis of turbidity and SS characteristics of different water bodies, providing data support for the formulation of environmental standards;
Third party testing: Compliance testing and reporting of indicators for enterprise discharge water, surface water, and drinking water.
The importance of detecting these parameters
- Preserving water supply Turbidity, the “intuitive ruler” of microbiological safety, conceals viruses and bacteria, reducing disinfection and endangering human health. Accurate monitoring guarantees that water distribution satisfies terminal water consumption safety requirements.
- Honor the surroundings
SS and turbidity are limited by the “Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard” (GB 8978-1996) and the “Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard” (GB 3838-2002). Organizations can avoid fines and meet environmental regulations by keeping an eye on compliance. - Improve processes
Sludge accumulation, aeration, chemical use, and wastewater treatment plant costs are all decreased by maintaining MLSS levels.
increased production efficiency, quicker discharge or filtration, longer equipment life, and real-time industrial circulation water turbidity and SS monitoring. - Preservation of the environment
Monitors can detect pollutants, prevent water damage, and safeguard ecosystems. The ecology and photosynthesis of aquatic plants are harmed by heavy suspended particles that reduce the clarity of surface water.
Quick Comparison: Which Technology Do You Need?
| Feature | Turbidity (NTU) | SS / MLSS (mg/L) |
| Primary Method | 90° Light Scattering | Infrared Absorption / Backscattering |
| Typical Range | 0.01 – 1000 NTU | 0 – 50,000 mg/L (or 5% concentration) |
| Water Type | Drinking water, filtered water, pool water | Raw sewage, activated sludge, industrial waste |
| Light Source | White light or Infrared LED | Near-Infrared (860nm LED) |
| Key Advantage | High precision for clear water | Unaffected by water color or high density |
Technical Support
How to Raise pH in Pool: The Chemical Guide & The Automated Solution
How to Calibrate pH Meter: A Step-by-Step Guide for Accurate Readings
Top 5 Heavy-Duty Plastic pH Electrodes for Wastewater (2026)
In complex water treatment processes, turbidity, SS, and MLSS are not just numbers on the screen, they are the “eyes” that ensure process stability, reduce operating costs, and protect environmental compliance.
From the pursuit of extremely low turbidity in water plants to the monitoring of viscous sludge in biochemical aeration tanks, every drop of water changes the overall situation. Choosing Sino Inst means that you are not only choosing high-precision optical sensors, but also a complete solution that can deal with bubble interference, film fouling, and chemical corrosion.
Request a Quote
.png)