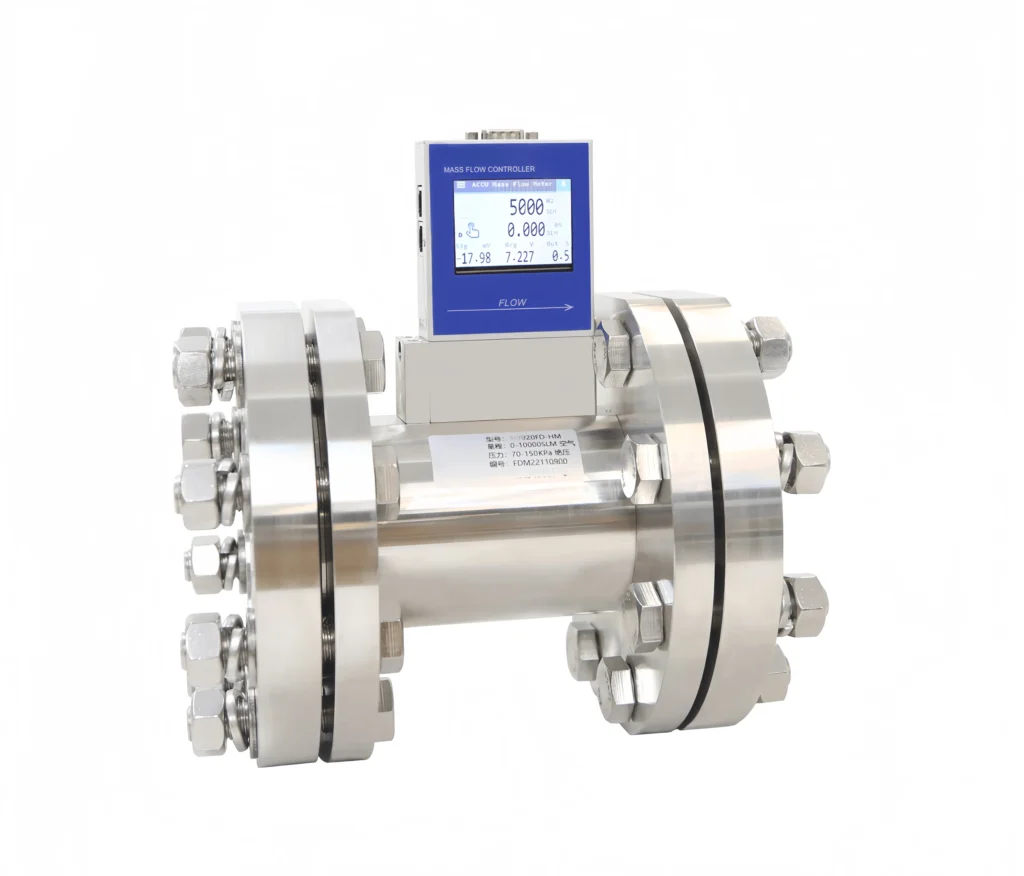
The SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter boasts an ultra-large measurement range. Measurement range: 6000 SLM~20000 SLM, accuracy: ±0.5%. Response time: 0.1s. Capable of measuring a variety of gases.
Sino-Inst is committed to technological research and development as the foundation of its company’s growth, providing customers with professional services for the measurement and control of flow rates of gases, liquids, and critical fluids. Simultaneously, we have a dedicated R&D and customization department to meet the personalized customization needs of some customers, such as “small-batch non-standard operating conditions.”
★★★★★
Features
Specifications
| Product Model | SI-20FD-HM |
| Measurement Range | 6000SLM~20000SLM |
| Control Range | Flow measurement range ratio 100:1 |
| Accuracy | ±0.5%F.S |
| Linearity | ±0.5%F.S |
| Repeatability | ±0.2%F.S |
| Response Time | Flowmeter: <0.1s |
| Flow controller: <0.2s | |
| Digital Input | RS232/485, MODBUS protocol |
| Analog Input | 0–5V, 4–20mA, 1–5V |
| Power Supply | ±15VDC, 24VDC |
| Operating Temperature | 0–50°C |
| Operating Pressure | Operating Differential Pressure: 0.3–0.5MPa |
| Maximum Pressure Rating | 3MPa/10MPa |
| Electrical Connection | DB9 Port, RJ11, 5.5×2.1 Power Quick Connector |
| Leak Rate | 1×10⁻⁹ Pa m³/s |
| Temperature Coefficient | ±0.025% F.S./°C |
| Base Material | Stainless steel |
| Seal Material | Fluorocarbon rubber, neoprene, nitrile rubber |
| Connector | φ12, 1“, 2”, flange mounting |
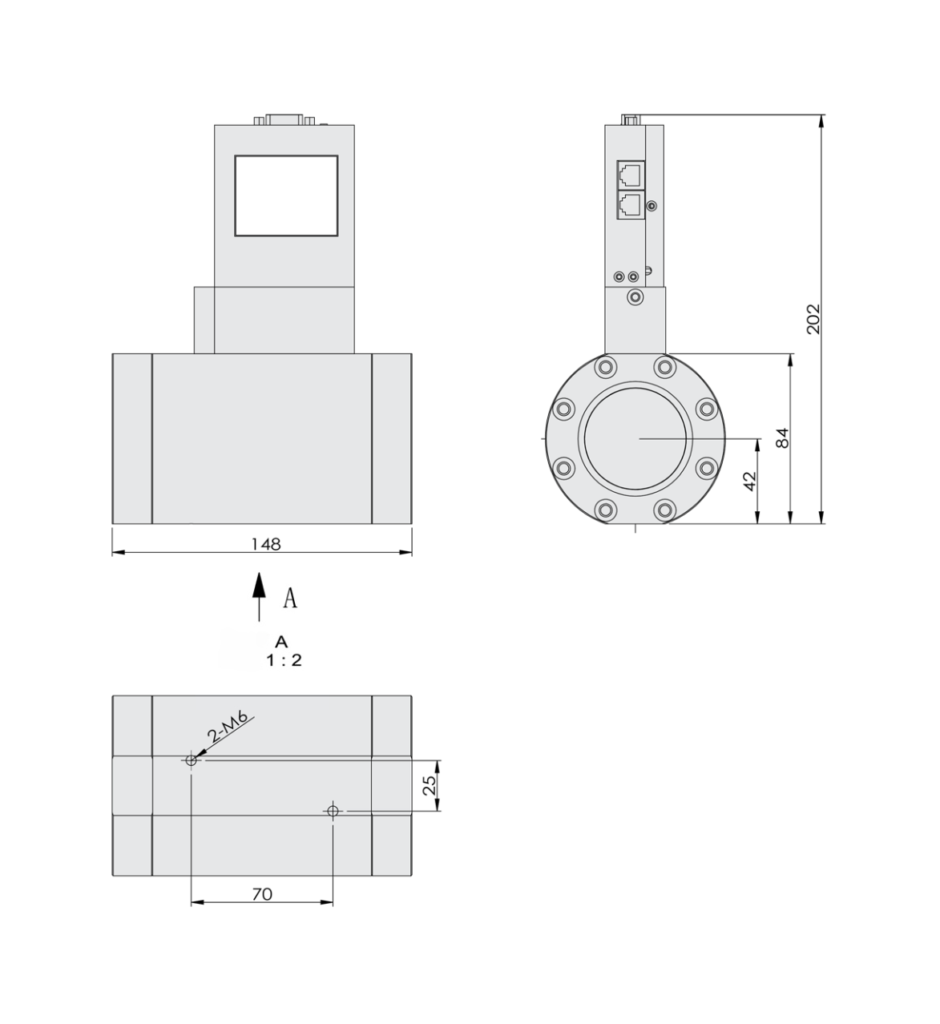 SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter without Flange Dimensions
SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter without Flange Dimensions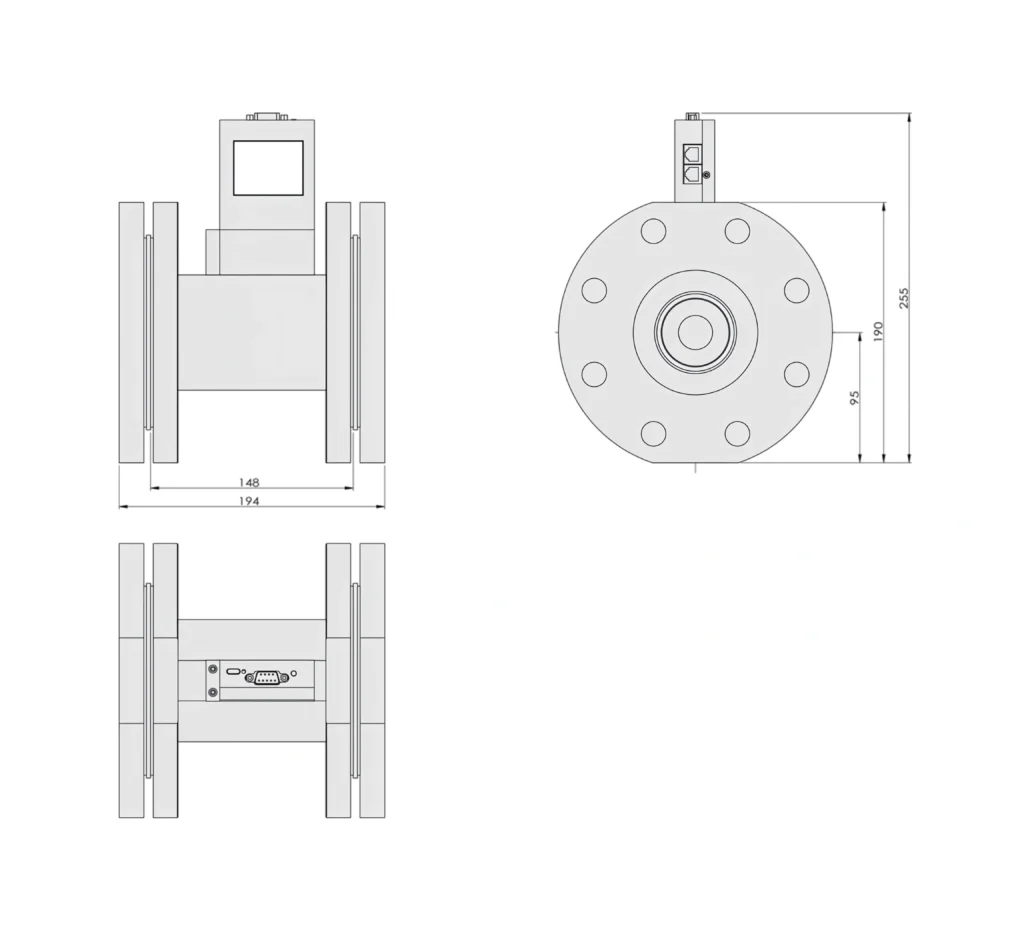 SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter with Flange Dimensions
SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter with Flange Dimensions
Featured Applications
Mass flow controllers are highly accurate, fast, reliable, stable, and flexible flow measurement instruments. Employing thermal sensing technology, they measure flow by detecting the mass of molecules carried away by the split molecular stream. Since this measurement relies on thermal sensing, it remains unaffected by changes in gas temperature or pressure. These controllers are used for measuring and regulating the mass flow of gases.
It will find increasingly widespread application in petroleum processing, chemical engineering, and related fields, demonstrating significant potential in advancing flow measurement technology. This instrument combines detection and control functions, incorporating an electromagnetic or piezoelectric control valve alongside its measurement component. This configuration forms a closed-loop system for regulating fluid mass flow. Setpoints can be supplied via analog voltage, analog current, or computer/PLC interfaces.
Thermal mass flow controllers are extensively applied in the following industries:
- Measurement and control of fuel gas mass flow in boilers and cracking furnaces;
- Mass flow measurement of petrochemical, petroleum production, and flare gases;
- Measurement and control of combustion furnace air mass flow; hydrogen mass flow and control in gas turbines;
- Mass flow and control of gases in food processing and beverage production;
- Chlorine mass flow control in water treatment plants;
- High-purity gas mass flow measurement in semiconductor manufacturing processes;
- Mass flow measurement of catalysts and chemical additives;
- Pump protection control, pump seal monitoring, and lubricant sump leak detection;
- HVAC system control;
- Mass flow measurement of instrument air, process air, nitrogen, etc.;
- Gas analyzers and atmospheric samplers;
- Leak monitoring
- Gas distribution systems
- Laboratory gas measurement
- Medical applications
- Fuel cells
Mass Flow Controller Gas Correction Factor
Sino-Inst mass flow controllers and mass flow meters are generally calibrated with N2 at the factory. In actual use, if other gases are being used, reading correction may be necessary. This is done by multiplying the flow rate displayed on the flow meter by the flow conversion coefficient.
For single-component gases, the conversion coefficient can be found in the coefficient conversion table.
For a multi-component gas (assuming it consists of n gases), calculate its conversion using the following formula:
Coefficient C: Basic Formula: C = 0.3106N/ρ(Cp)
Where:
ρ—density of the gas under standard conditions
Cp—specific heat at isobaric pressure of the gas
N—molecular composition coefficient of the gas (related to the components of the gas molecules, see the table below)
| Gas Molecule Composition | For example | N values |
| Monoatomic Molecules | Ar He | 1.01 |
| Diatomic Molecules | CO N2 | 1.00 |
| Triaatomic Molecules | CO2 NO2 | 0.94 |
| Polyatomic Molecules | NH3 C4H8 | 0.88 |
For a gas mixture: N = N1(ω1/ωT) + N2(ω2/ωT) + … + Nn (ωn /ωT)
Where:
ω1…ωn—flow rate of the corresponding gas
ωT—flow rate of the gas mixture
ρ¹…ρn—density of the corresponding gas under standard conditions (values see the gas conversion coefficient table)
Cρ¹…Cρn—specific heat at isobaric pressure of the corresponding gas (values see the gas conversion coefficient table)
N1…Nn —These are the molecular composition coefficients for the corresponding gases; values can be found in the Gas Molecular Composition Coefficients Table.
Notes:
1) Standard conditions: Pressure—101325 Pa (760 mmHg), Temperature—273.15 K (0℃).
2) For parameters of gases not listed in the Gas Mass Flow Rate Conversion Coefficients Table, please consult Sino-Inst.
Common Gas Correction Factors:
| Gases | Code | Specific heat (cal/g/°C) | Density (g/L 0°C) | Conversion factor |
| Air | 8 | 0.24 | 1.293 | 1.006 |
| Ar Argon | 4 | 0.125 | 1.7837 | 1.415 |
| AsH3 Arsenic hydride | 35 | 0.1168 | 3.478 | 0.673 |
| BBr3 Boron tribromide | 79 | 0.0647 | 11.18 | 0.378 |
| BCl3 Boron trichloride | 70 | 0.1217 | 5.227 | 0.43 |
| BF3 Boron trifluoride | 48 | 0.1779 | 3.025 | 0.508 |
| B2H6 Borane | 58 | 0.502 | 1.235 | 0.441 |
| CCl4 Carbon tetrachloride | 101 | 0.1297 | 6.86 | 0.307 |
| CF4 Carbon tetrafluoride | 63 | 0.1659 | 3.9636 | 0.42 |
| CH₄ Methane | 28 | 0.5318 | 0.715 | 0.719 |
| C₂H₂ Acetylene | 42 | 0.4049 | 1.162 | 0.581 |
| C₂H₄ Ethylene | 38 | 0.3658 | 1.251 | 0.598 |
| C₂H₆ Ethane | 54 | 0.4241 | 1.342 | 0.481 |
| C₃H₄ Propyne | 68 | 0.3633 | 1.787 | 0.421 |
| C₃H₆ Propene | 69 | 0.3659 | 1.877 | 0.398 |
| C₃H₈ Propane | 89 | 0.399 | 1.967 | 0.348 |
| C₄H₆ Butyne | 93 | 0.3515 | 2.413 | 0.322 |
| C₄H₈ Butene | 104 | 0.3723 | 2.503 | 0.294 |
| C₄H₁₀ Butane | 111 | 0.413 | 2.593 | 0.255 |
| C5H12 Pentane | 240 | 0.3916 | 3.219 | 0.217 |
| CH3OH Methanol | 176 | 0.3277 | 1.43 | 0.584 |
| C2H6O Ethanol | 136 | 0.3398 | 2.055 | 0.392 |
| C2H3Cl3 Trichloroethane | 112 | 0.1654 | 5.95 | 0.278 |
| CO Carbon monoxide | 9 | 0.2488 | 1.25 | 1 |
| CO2 Carbon dioxide | 25 | 0.2017 | 1.964 | 0.737 |
| C2N2 Cyanogen | 59 | 0.2608 | 2.322 | 0.452 |
| Cl2 Chlorine | 19 | 0.1145 | 3.163 | 0.858 |
| D2 Deuterium | 14 | 1.7325 | 0.1798 | 0.998 |
| F2 Fluorine | 18 | 0.197 | 1.695 | 0.931 |
| GeCl₄ Tetrachloride germanium | 113 | 0.1072 | 9.565 | 0.267 |
| GeH₄ Germanium hydride | 43 | 0.1405 | 3.418 | 0.569 |
| H₂ Hydrogen | 7 | 3.4224 | 0.0899 | 1.01 |
| HBr Hydrogen bromide | 10 | 0.0861 | 3.61 | 1 |
| HCl Hydrogen chloride | 11 | 0.1911 | 1.627 | 1 |
| HF Hydrogen fluoride | 12 | 0.3482 | 0.893 | 1 |
| HI Hydrogen iodide | 17 | 0.0545 | 5.707 | 0.999 |
| H₂S Hydrogen sulfide | 22 | 0.2278 | 1.52 | 0.844 |
| He Helium | 1 | 1.2418 | 0.1786 | 1.415 |
| Kr Krypton | 5 | 0.0593 | 3.739 | 1.415 |
| N₂ Nitrogen | 13 | 0.2468 | 1.25 | 1 |
| Ne Neon | 2 | 0.2464 | 0.9 | 1.415 |
| NH3 Ammonia | 29 | 0.5005 | 0.76 | 0.719 |
| NO Nitric oxide | 16 | 0.2378 | 1.339 | 0.976 |
| NO2 Nitrogen dioxide | 26 | 0.1923 | 2.052 | 0.741 |
| N2O Nitrous oxide | 27 | 0.2098 | 1.964 | 0.709 |
| O2 Oxygen | 15 | 0.2196 | 1.427 | 0.992 |
| PCl3 Phosphorus trichloride | 193 | 0.1247 | 6.127 | 0.358 |
| PH3 Phosphine | 31 | 0.261 | 1.517 | 0.691 |
| PF5 Phosphorus pentafluoride | 143 | 0.1611 | 5.62 | 0.302 |
| POCl3 Phosphorus oxychloride | 102 | 0.1324 | 6.845 | 0.302 |
| SiCl4 Silicon tetrachloride | 108 | 0.127 | 7.5847 | 0.284 |
| SiF₄ Silicon tetrafluoride | 88 | 0.1692 | 4.643 | 0.348 |
| SiH₄ Silane | 39 | 0.3189 | 1.433 | 0.599 |
| SiH₂Cl₂ Dichlorosilane | 67 | 0.1472 | 4.506 | 0.412 |
| SiHCl₃ Trichlorosilane | 147 | 0.1332 | 6.043 | 0.34 |
| SF₆ Sulfur hexafluoride | 110 | 0.1588 | 6.516 | 0.264 |
| SO₂ Sulfur dioxide | 32 | 0.1489 | 2.858 | 0.687 |
| TiCl₄ Titanium tetrachloride | 114 | 0.1572 | 8.465 | 0.206 |
| WF₆ Tungsten hexafluoride | 121 | 0.0956 | 13.29 | 0.215 |
| Xe Xenon | 6 | 0.0397 | 5.858 | 1.415 |
Technical Support
5 Best Digital Mass Flow Controllers for Precision Gas Flow Measurement
Guide to Connecting a Thermal Mass Flow Controller to a PLC
Sino-Inst’s High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter is configurable with a large flow range of 6000 SLM to 20000 SLM for gas flow measurement and control. It is widely used in the glass, solar energy, petrochemical, coal metallurgy, gas production and distribution, and hydrogen energy industries.
We support customization of mass flow meters/controllers, including flow range, temperature, pressure, accuracy, and materials. Please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
Request a Quote
SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter 6000~20000SLM

The SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter boasts an ultra-large measurement range. Measurement range: 6000 SLM~20000 SLM, accuracy: ±0.5%. Response time: 0.1s. Capable of measuring a variety of gases.
Product SKU: SI-20FD-HM High Accuracy Mass Flow Meter Ultra-Large Range
Product Brand: Sino-Inst
Price Valid Until: 2099-09-09
Product In-Stock: PreOrder
5
.png)






